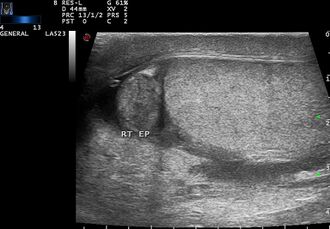
Acute epididymitis
Acute epididymitis is an inflammatory disease of the epididymis, which is the most common cause of acute scrotal syndrome in adults.
Etiology and pathogenesis[edit | edit source]
In most cases, the cause of Epididymitis is a urinary tract infection. Inflammation can also enter the epididymis canalicularly during acute prostatitis or urethritis, by transfer from surrounding inflamed organs, Hematogenously or Iatrogenically after cystoscopy, TUR and other procedures.
Clinical picture[edit | edit source]
Inflammation of the epididymis is manifested by a gradually increasing swelling of half of the scrotum and reddening of the skin with significant pain along the vas deferens, which propagates to the groin and is accentuated by movement. Fever, general malaise, and a positive Prehn's sign (pain subsides when the testicle is lifted) will help differentiate epididymitis from testicular torsion.
Diagnostics[edit | edit source]
The basis is the anamnesis and the typical clinical picture. A positive urine culture, leukocytosis and an increase in inflammatory parameters in the blood, increased sedimentation and a typical image during an ultrasound examination - thickened epididymis of inhomogeneous structure and often a secondary hydrocele - subsequently contribute to the correct diagnosis .
In the differential diagnosis, we also consider torsion of the testicle , torsion of the appendix of the testicle , hematocele, hydrocele, tumor of the testicle, contracted scrotal hernia, chronic scrotal hernia, tuberculosis of the epididymis
Treatment[edit | edit source]
Rest, padding of the scrotum or suspensor, local cold compresses, broad-spectrum ATB , analgesics and antipyretics are recommended. In the case of an abscessed form, incision and drainage to accelerate healing, in case of recurrences of epididymectomy or orchiectomy.
Complications[edit | edit source]
Complications of Acute Epididymitis are testicular infarction, development of chronic pain, infertility. The prognosis is good with timely treatment, in neglected conditions there is a risk of the necessity of surgical removal of the organ.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Used literature[edit | edit source]
- DVOŘÁČEK, Jan. Urologie : obecná a speciální urologie. 2. edition. Praha : Karolinum, 1999. pp. 224−225. ISBN 80-7184-745-3.