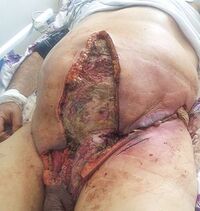
Fournier's gangrene
Fournier's gangrene is a rare but very serious polymicrobial infection of the male genitalia, leading to fasciitis and gangrene of soft tissues in the area. It is one of the most serious conditions in urology. This is a superficial process affecting the skin of the scrotum or penis (the testicles are not affected). The perineum and perianal area may also be affected. Fournier gangrene is a disease associated with a high mortality.
Etiology[edit | edit source]
The cause of Fournier's gangrene is a polymicrobial infection that spreads from the anorectum, urogenital tract, or external genitalia. It often arises as a result of urological or colorectal disease, or surgery in these areas. It can also be the result of an external injury of the prostate or urethra, or from endoscopichemorrhoids or perianal fistula surgery. Predisposing factors are immunodeficiency, malnutrition, alcoholism, tumor cachexia, diabetes mellitus and other conditions leading to the weakening of the organism. The cause of the infection is usually a mixture of microbial flora with a predominance of anaerobes.
Clinical picture and diagnostics[edit | edit source]
Fournier gangrene is a peracute disease. It is accompanied by fever, chills and pain in the genitals. The clinical picture includes swelling of the testicles (in advanced forms with invasion to the lower abdomen) with crepitation in the subcutaneous tissue (gas-forming bacteria). Examination of the blood count shows leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia, and coagulation disorders. Creatinine levels are high as well.
Therapy[edit | edit source]
If Fournier gangrene is suspected, hospitalization of the patient and intensive comprehensive treatment are indicated. Broad-spectrum antibiotics covering the entire bacterial spectrum, including aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, are immediately administered. Urgent surgical treatment with necrotomy (necrectomy) of all gangrenous tissues, peroxide lavages, drainage, and anti-inflammatory and anti-tetanus sera are necessary. Hyperbaric therapy in case of extensive penile involvement is also necessary.
Combination of antibiotics in gangrenous genital infection[edit | edit source]
- Aminoglycosides
- beta-lactam antibiotics (e.g., cephalosporins generation III)
- always metronidazole (for anaerobes)
Prognosis[edit | edit source]
The prognosis of the disease is poor. Even with immediate and aggressive therapy, Fournier's gangrene has a 50% mortality rate.
References[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Used Literature[edit | edit source]
- DVOŘÁČEK, Jan. Urologie : obecná a speciální urologie. 2. vydání. Praha : Karolinum, 1999. s. 224-225. ISBN 80-7184-745-3.
- HERÁČEK, Jiří a Michael URBAN, et al. Urologie pro studenty : Akutní skrotální syndrom [online] . 2.0. vydání. 2012. Dostupné také z <http://www.urologieprostudenty.cz/uploads/pdf/akutni-skrotalni-syndrom.pdf>. ISBN 978-80-254-1859-8.
Recommended Literature[edit | edit source]
- HANUŠ, Tomáš. Urologie. 1. vydání. V Praze : Triton, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7387-387-5.
- MACEK, Petr a Tomáš HANUŠ. Urologie : pro všeobecné praktické lékaře. 1. vydání. Praha : Raabe, 2011. ISBN 9788086307855.