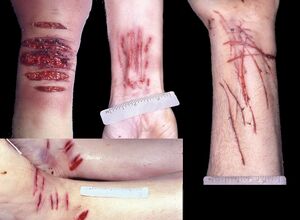
Incision wounds
Incision wounds develop by thrust and pressure of a sharp instrument in the direction of its long axis over the surface of the body.
Charakteristics[edit | edit source]
The wounds are longer than they are wide, their edges are clean, angles are sharp. Deepest place is in the middle or closer to the angle in which direction they were led, and where they end. In the angles they are more shallow. If the cut was caused by a saw, the edges are serrated. The wounds are usually straight or slightly arcuate, if the tool was applied diagonally to the
body surface, they may be more arcuate to lobed. With tangential action, the skin flap can be cut off and an oval skin defect is created. The wound may also be intermittent if the instrument has only superficially cut wrinkled or folded skin. The width of the wound depends mainly on the course of the cut elastic fibres of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. If the elastic fibres are cut transversely, the edges are retracted and the wound is more gaping. Similarly, if the wound extends into the musculature and the muscle fibres have been cut transversely, the wound is more open. The depth of the wound depends, besides the sharpness, on the intensity of the instrument applied. Incision wounds usually don't affect the bone, only periost and rarely surface bone lammela are cut. Saw wounds penetrate much deeper. Incision wounds bleed extensively. If larger vessels are injured, death occurs due to bleeding out. In incision wounds of the neck often air embolism occurs and in wound of the trachea blood aspiration occurs. Infectious complications are not common, because heavy bleeding lowers the danger of infection.
The ability to act[edit | edit source]
The ability to act even in deadly incision wounds is sometimes maintained for a longer period of time. The injured person can still walk around the apartment, run down the stairs, go out of the house, etc. Even with deep cuts to the neck with injury to the carotids the ability to act may be maintained for a period of time. In these cases, extensive blood traces are found in various places at the scene, raising suspicions about the other person's actions and the crime of murder.
Instrument identification[edit | edit source]
Identification of the tool from the nature of the wound is usually impossible because the incision wound has few characteristic features of the tool used. Wounds caused by scissors (shear wounds) are V-shaped, with a flat defect produced by tangential action.
Murder/Suicide/An unfortunate event[edit | edit source]
Murder[edit | edit source]
Murder incision wounds are most common on the neck and back of the head, but they can be on any part of the body. They tend to be led through clothing. It is usually one deep wound, More rarely, there are several, especially if the killing was preceded by a struggle and the victim's torment. In this case, they are not parallel to the main wound, which most often runs horizontally on the neck. On the victim's hands and fingerssigns of self-defensemay be found , most often transversely running, often lobulated incisional wounds, sometimes quite deep. Only one wound may be visible on the neck, and there may be several deep wounds with incisions on the spine. Cut wound murders are most often committed on persons who are drunk, drugged or asleep.
Suicide[edit | edit source]
Suicidal incision wounds are most often located on the wrists, forearms, elbow sockets, neck, possibly in the knee sockets and on the back of the calves, around the ankles and on the abdomen. They tend to be on uncovered orexposed and accessible parts of the body. Typical of suicide wounds are superficial cuts of the skin at one of the angles of the main wound. The suicide either did not have the courage to wound himself deeply immediately or was looking for the best place to insert the instrument. If there are several incisions, they tend to be parallel, as the limb is held in the same position and the instrument is repeatedly guided in the same direction. In right-handed people, the wounds are located on the left upper limb or on the left side of the neck. On the wrists, forearms and elbow sockets the wounds are usually transverse, on the neck slightly oblique from the back to the top and down. On the neck, the cuts can be very deep, especially when a sharp instrument is used. Large neck vessels , larynx, trachea and esophagus may be severed, so the wounds reach the spine, which has a cut in the periost. The deepest cuts are on the neck and abdomen.
An unfortunate event[edit | edit source]
Accidental cuts are most common and occur in household and occupational settings. They are mainly found on the hands. In the face, together with minor stab wounds, they are caused by glass fragments in traffic accidents and by the victim hitting the windscreen.
Sexual deviation[edit | edit source]
- Sadism
Incision wounds in sadism are usually on different parts of the body and may be combined with stab wounds or other injuries. They often affect the breasts and genitalia, which may be cut off.
- Masochism
In masochism the wounds are superficial and only on the parts of the body, which the masochist can reach.
Others[edit | edit source]
Cut wounds can also be encountered when dismembering the body for easy removal. They are most common in the neck and hip and shoulder joints.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Used literature[edit | edit source]
- ŠTEFAN, Jiří – HLADÍK, Jiří. Soudní lékařství a jeho moderní trendy. 1. edition. Grada, 2012. ISBN 978-80-247-3594-8.