Topographic formations of the back
The topographic formations of the back include : vertebral canal, inferior lumbar triangle, superior lumbar triangle and suboccipital triangle.
Vertebral canal[edit | edit source]
Vertebral canal (lat. canalis vertebralis) is a tubular space that is formed by the vertebral foramina (lat. foramina vertebralia) of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar vertebrae.
Its content is mainly the spinal cord, spinal cord meninges and spinal cord vessels.
Boundary of the topographical formation:
- cranially − foramen magnum,
- caudally − sacral hiatus,
- ventrally − vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs,
- dorsally − vertebral arches and their laminae and ligg. interarcualia (flava).
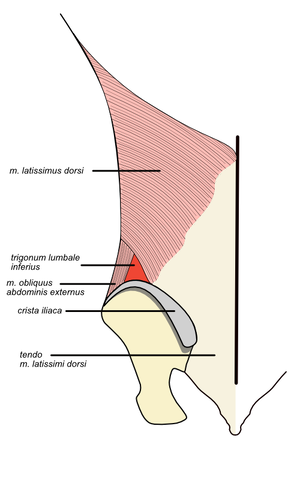
Inferior lumbar triangle[edit | edit source]
Inferior lumbar triangle of Petit is located above the crest of the pelvic bone (crista iliaca). Its contents may include lower lumbar hernias (hernias), which make up up to 5% of hernias.
Boundaries:
- caudally − crista iliaca of the pelvic bone,
- medially − latissimus dorsi muscle,
- laterally − musculus obliquus externus abdominis,
- bottom − musculus obliquus internus abdominis.
Superior lumbar triangle[edit | edit source]
Superior lumbar triangle of Grynfeltt and Lesshaft is the site of penetration of lumbar hernias (up to 95%). Another content of the topographic site is iliohypogastric nerve, subcostal nerve and subcostal vessels.
Another name for this formation is the tetragonum of Kraus (if we include the craniolaterally located 12th rib in its boundaries).
Boundaries:
- cranially - serratus posterior inferior muscle,
- medially − iliocostalis lumborum muscle,
- laterally − musculus obliquus internus abdominis,
- ceiling - latissimus dorsi muscle.
Suboccipital triangle[edit | edit source]
Suboccipital triangle is located in the posterior cervical region (nuchal region).
Contains structures: vertebral artery, suboccipital nerve, greater occipital nerve.
Boundaries :
- medially − rectus capitis major muscle,
- laterally − musculus obliquus capitis superior,
- caudally − musculus obliquus capitis inferior.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
- Topography of the chest
- Topographic formations of the upper limb
- Topographic anatomy of the hand and fingers
External links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- GRIM, Miloš – DRUGA, Rastislav, et al. Základy anatomie : 5. Anatomie krajin těla. 1. edition. Galén, 2008. 119 pp. ISBN 978-80-7262-179-8.
- ANONYMOUS AUTHOR, Performing under the pseudonym Starý medik. Topografic locations in the back [online]. ©2011. [cit. 2017-07-20]. <http://www.uzdravim.cz/topograficka-mista-na-zadech.html>.