Hormonal anticonception
Puberty in a woman is manifested by the development of secondary signs and the onset of menstrual cycle. All the changes that complete its image are conditioned by the fluctuating secretion of estrogens' and gestagens from ovaries.
The endocrine function of the ovaries' is controlled by the regular cyclic release of pituitary hormones: FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone). Macroscopically, the beginning of the cycle is considered to be menstruation (bleeding) conditioned by the shedding of the upper layers of the endometrium. On the 6th day, FSH secretion rises. Under its influence, follicle maturation in the ovaries is started. The thecal cells of follicles produce estrogens. LH levels also rise mid-cycle. The follicle bursts and releases the egg into the abdominal cavity near the fallopian tube. The cavity of the follicle is filled with blood and fluid (corpos haemorrhagicum) and later the cavity is filled with proliferating theca cells (corpus luteum). At the same time, progesterone production rises.
The endometrium in the first phase under the influence of estrogens proliferates greatly (proliferative phase), after ovulation with an increase in progesterone, the glands multiply and the mucous membrane is prepared for implantation of the egg (secretory phase ). If fertilization does not occur, the upper layer of the endometrium separates - menstrual bleeding.
Estrogens
The major estrogen in humans is estradiol. Other physiologically active are estrone and estriol . As these substances belong to the category of steroid hormones (hydrophobic), they are almost 100% transported in the blood bound to the so-called SHBG (sex hormone binding protein, globulin). Although oral estradiol is active after oral administration, it is better to use semisynthetic derivatives (mainly ethinyl estradiol ) for the high first-pass effect .
Effects on tissues
Estrogens are essential for normal adolescence and sexual develompmennt. Under their influence, the reproductive organs grow and secondary sexual characteristics develop. Metabolic effect - in the plasma reduces the amount of cholesterol - increase TAG and decrease LDL ( lipoproteins of low density) particles (less incidence of cardiovascular disease in women of reproductive age), reduce osteoclast activity (preventing osteoporosis), increased coagulation(increased synthesis of fibrinogen in the liver) .
Clinical use
- Replacement therapy – treatment of hypogonadism in girls, prevention of postmenopausal changes in women - beneficial effect against atrophy of the uterus (vagina, uterus) and osteoporosis, less effective in the treatment of hot flushes (attacks of redness in the face and upper torso, associated with mental instability); hypertension must be affected only by symptomatic treatment;
- hormonal contraception – in combination with progestagens to prevent conception or induce death of a fertilized egg; high doses are used once as the so-called morning after contraception (not completely accurate labeling, as it often does not prevent the conception itself, but it has an abortifiable effect and thus prevents the development of pregnancy)
- prostate cancer – palliative treatment.
Toxicity
There is mainly a stimulating effect on the vagina, uterus and mammary glands. Medium doses lead to breast tension, endometrial hyperplasia and subsequent excessive bleeding . They can have a teratogenic effect when given during pregnancy. Long-term estrogen use is also associated with more frequent gallbladder disease.
Progestogens
| corpus luteum, placenta |
Progestogens ( progestins ) form group female sexual hormones with anti- estrogenic and anti- gonadotropic effect . The most important is progesterone .
Progesterone
It is formed in the corpus luteum ovaries and placenta ( after 6–8 weeks pregnancy ; 30–40x more ), as intermediate product synthesis of androgens and estrogens also in the cortex of the adrenal gland and in the small amount in testes.
synthesized from cholesterol . over intermediate product pregnenolone , from which it differs in arrangement on A circle .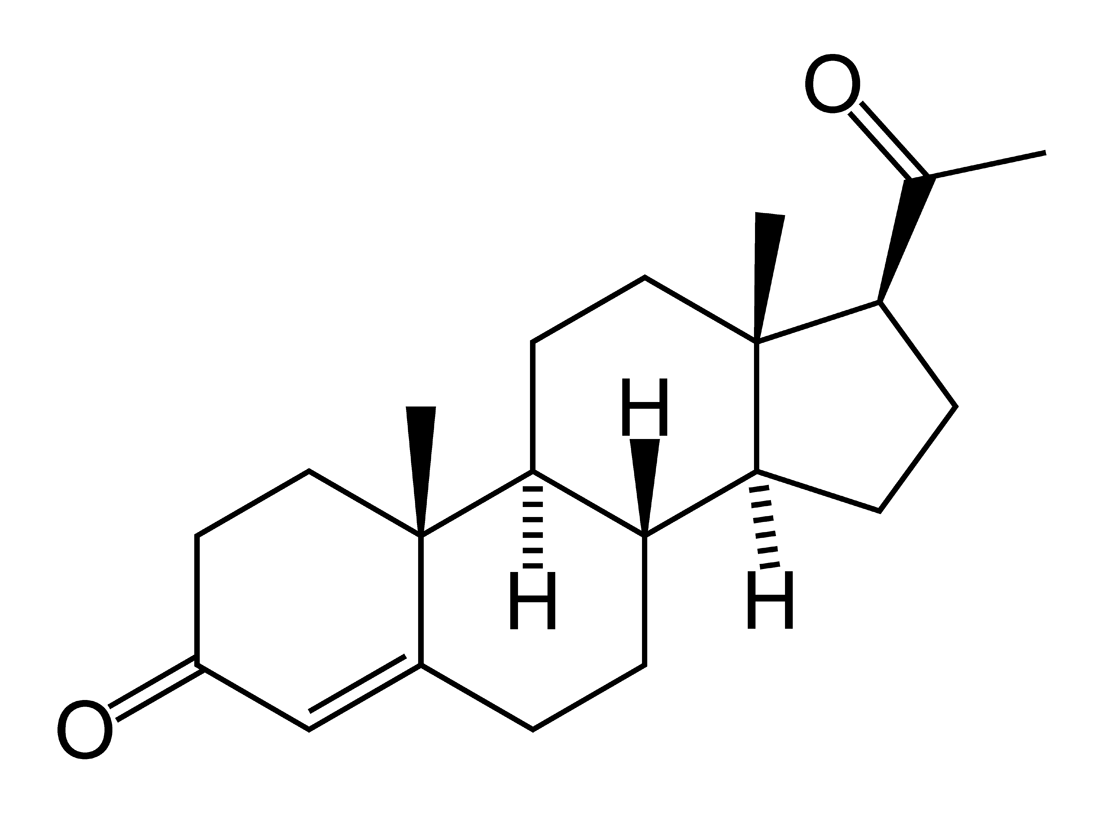 It binds in plasma on proteinaceous carrier . It is fast in the liver . metabolized – has very low biological availability and short biological half time . Due to active metabolism in the liver is progesterone after ineffective .
It binds in plasma on proteinaceous carrier . It is fast in the liver . metabolized – has very low biological availability and short biological half time . Due to active metabolism in the liver is progesterone after ineffective .
After conjugation with an acid glucuron ( inactivation ) in the liver form pregnanediol excludes urine .
Effect
Progestins lead to:
- development secretory tissue in breasts glands ( acini ) – lactation is , however blocked and starts until after birth u ( violent decrease levels progesterone ), maintained prolactin em
- maturation of the endometrium in the second half menstrual menstrual cycle cycle – transition from proliferative to secretory phase ( zoom volume and size secretion glands and increased content glycogen u ) -> preparation uterine mucosa for reception ova + constriction throats and thickening cervical mucus .
- reduction effects of estrogens on vaginal the wall
- influence peripheral flow rate blood - reduce thermal losses , i.e. increases physical temperature (on average by 0.5& nbsp;° C during luteal phase cycle – indicator ovulation )
Compared to [ [ estrogens ]] they have minimal effect on song plasma proteins ( do not affect plasma fibrinogen levels ) . _ Significantly they influence metabolism sugars and stimulate saving fats .
Progestogens and estrogens acts synergistically – estrogens they initiate creation receptors for progesterone .
Clinical using
Main the indication is application as part of contraception . In the long run are also applied they can use to long term suppression of [[ovaries|ovaries ] ] e.g. in endometriosis . They don't have effect on invocation abortion u. Toxicity of progestins is low , though they can to condition rise blood pressure and a drop in HDL.
Like oral contraceptives are used too synthetic steroids – derivatives of 17alpha-hydroxyprogesterone and 17alpha-alkyl- substituted derivatives of 19-nortestosterone, medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera) etc. Inhibitory effect on grow cells is used on treatment differentiated endometrial cancer . < noinclude >
Links
Related Articles
References
Template:Navbox - hormony Template:Pahýl </noinclude>
Contraception
Birth control history
- The effort to separate sexual life from the conception of a child is as old as humanity itself - the legendary biblical Onan - "whenever he went in to a woman, he let his seed fall on the ground so that he would not produce offspring" (Genesis 38:9) - the mentioned biblical hero thus became an inventor not masturbation, but the oldest contraceptive methods - interrupted intercourse.
- Advice from the ancient Egyptians: introduce various substances into the vagina before intercourse: Petri papyrus, paste made from crocodile dung, elephant dung, ox bile,... The method based on the principle of killing sperm is still used today in contraceptive suppositories (of course, it does not contain these substances).
- History of modern contraception: 1921 – Haberlandt (Austria) noticed that extracts from the ovaries of pregnant animals could be used as contraception. However, 80,000 ovaries would be needed to obtain a dose for one female user.
- Synthesis of artificial hormones - American chemist Russel Marker from the extracts of a certain Mexican plant.
- 1960 – the first contraceptive tablet Enavid 10 on the market – high hormone content – one tablet contains estrogens for 10 days and progestogens for 20.
Interrupted intercourse – coitus interruptus
- The method is not very reliable - up to 20% failure per year. Causes of failure:
- leakage of sperm can occur even without a male orgasm;
- expulsion of sperm outside the vagina can also be a source of pregnancy;
- after ejaculation, a small amount of sperm remains in the urethra, and during repeated intercourse, a couple always enters the vagina.
- The method should remain an emergency solution, reserved for situations where there really is nothing else available.
The Ogino-Knaus method
- Counting fertile and infertile days. The method requires a regular menstrual cycle and it is recommended to monitor ovulation by measuring the basal temperature.
Condom
- It was allegedly used by the famous Jacomo Casanova (1725–1798). Before World War II, more than one and a half million were produced annually in the US alone. Today's world production is at the level of 8.5 trillion pieces.
- It is relatively reliable and cheap protection. To a large extent, it also protects against the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases, which is why it is mainly recommended for those who do not have a permanent partner.
Cervical pessary
- cup-shaped, semicircular structure made of plastic, which is placed on the cervix. It must be of the appropriate size recommended by the doctor. It is not very popular here.
Chemical contraception
- Spermicide creams and suppositories are inserted before intercourse. Although they are healthy, harmless and easily available, they are relatively unreliable. They require an experienced user and are more suitable as a supplement to other contraceptive methods to increase reliability.
Intrauterine bodies
- An effective, long-term, convenient and cheap method. It has been used for many years and yet it is not known exactly how it works. It is especially suitable for women who have already given birth. It is not suitable for those who have heavy periods or frequently change partners.
Biphasic Hormonal Contraception
- Estrogen alone would not be enough because the lining of the uterus would grow and there would be irregular bleeding and an increased risk of cancer. Therefore, progestin is added towards the end of the cycle to prevent the growth of the endometrium and to close the cervix at the same time. Administering gestagens all the time is advantageous because the lining of the uterus does not grow, the cervix is closed - this is a double protection and thus it is possible to reduce the dose of estrogens.
Single-phase hormonal contraception
- Each tablet contains a dose of estrogens mixed with progestogens.
Contraceptive patches
- They are based on the same principle as combinov



