Fracture healing disorders
Fracture healing disorders include :
- prolonged healing;
- malunion;
- hinge.
Prolonged fracture healing[edit | edit source]
The term prolonged fracture healing means that the healing time is longer than the expected fracture healing (6-8 weeks).
It is in process:
- by prolonging immobilization ;
- in conservatively treated fractures with operative osteosynthesis ;
- sometimes spongioplasty is also performed.
Malunion[edit | edit source]
Malunion represents healing in a malposition.
- It can be asymptomatic or manifest as dysfunction ;
- arises during imperfect reposition or after unstable fixation ( redislocation - therefore repeated X-ray checks are necessary);
- osteotomy and osteosynthesis are performed in the correct position to prevent arthrosis from improper loading.
Paklub[edit | edit source]
A knock-on ( pseudarthrosis ) is characterized as a disorder of fracture healing, when bone fragments do not fuse together even in a time twice as long as the normal course of healing (until then, we are only talking about prolonged healing ).
The fracture line is filled with fiber and surrounded by a fibrous sheath that contains fluid.
Classification according to clinical findings[edit | edit source]
- weak : unstable, with great pathological mobility, cannot bear loads
- solid : without pathological momentum, withstands loads
Classification according to Čech and Weber[edit | edit source]
- Vital – insufficient stabilization and immobilization of the fracture, sufficient blood supply and tendency to healing..
- Hypertrophic ;
- normotrophic – occurs mostly in unstable osteosyntheses;
- oligotrophic – usually arises from overextended skeletal traction.
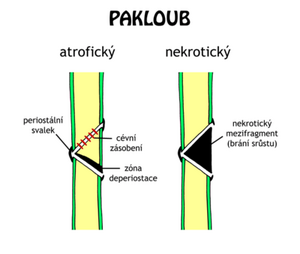
- Vital - insufficient blood supply, sclerotization or osteoporosis of bone ends.
- Dystrophic ;
- necrotic ;
- defective ;
- atrophic.
The most serious form is an infected joint - it occurs in all the above-mentioned forms and can lead to limb amputation. A special example is the tibial joint in fractures of the lower leg, where the fibula heals earlier and acts as a spacer (similarly, earlier healing of the ulna acts in fractures of the radius.
Links[edit | edit source]
[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- PASTOR, Jan. Langenbeck's medical web page [online]. [cit. 12.4.2010]. <https://langenbeck.webs.com/>.