Virus biochemistry
Viruses are infectious nucleic acid particles coated with a protective sheath. They behave like an intracellular parasite with the information for their own reproduction. However, they lack the ability to release energy from substances and are not equipped with a proteosynthetic apparatus. In their reproduction,they use metabolic and proteosynthetic mechanisms of the host cells.
Genetic material[edit | edit source]
Viruses contain either RNA or DNA , never both at the same time. There are only a few genes in their genome (QB virus has 4 genes, smallpox viruses 250 genes).
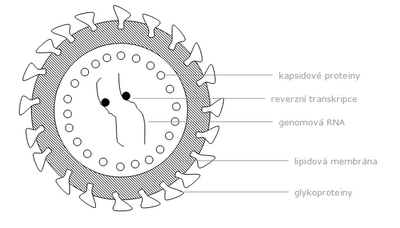
The complete extracellular product of viral reproduction is the viral particle. It consists of the viral nucleic acid, protected by a "capsid" consisting of many protein molecules (usually the protein molecules are the same). In more complex viruses, the virion is encased in a lipid mantle containing glycoproteins. In the virion, several molecules of specific viral enzymes, RNA primer and possibly other molecules needed to start reproduction are "packaged".
Virus reproduction[edit | edit source]
It is a model of synthesis and formation of cellular components. It proceeds according to a simple programme of gradual gene expression and gradual assembly of highly ordered structures formed by various macromolecules. According to the host, there are bacterial viruses (bacteriophages, phages) and zoopathogenic, or rather anthropopathogenic viruses. During infection, the virion either penetrates the cell and loses its mantle and capsid, or the nucleic acid is injected into the host cell while the rest of the virion remains extracellular. According to the type of genetic material, DNA viruses and RNA viruses are distinguished.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
- Viruses
- DNA viruses
- RNA viruses
- Reproduction of the DNA viruses
- Reproduction of the RNA viruses
- Interferons
Source[edit | edit source]
- ŠTÍPEK, Stanislav. Stručná biochemie : uchování a exprese genetické informace. 1. edition. Praha : Medprint, 1998. ISBN 80-902036-2-0.
Used literature[edit | edit source]
- ŠTÍPEK, Stanislav. Stručná biochemie : uchování a exprese genetické informace. 1. edition. Praha : Medprint, 1998. ISBN 80-902036-2-0.