Non-specific intestinal inflammations
Among the nonspecific intestinal inflammations' [1] include Crohn's disease (ileitis terminalis) and ulcerative colitis (proctocolitis idiopathica). These are chronic inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract, which are often accompanied by abundant extraintestinal symptoms. Both diseases begin in childhood or during adolescence and their etiology is unclear. The incidence and prevalence of non-specific intestinal inflammation has been increasing in recent years, 20-30% of patients are children under the age of 18.[2]
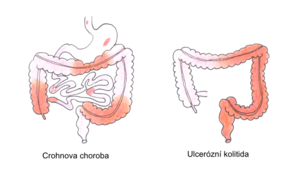
- Crohn's disease
It is a chronic non-specific inflammation of the small or large intestine (or any part of the GIT). It is segmental or multisegmental, transmural, in typical cases granulomatous inflammation.
- Ulcerative colitis
Non-specific hemorrhagic-catarrhal or ulcerative inflammation of the anus and the adjacent part (or the entire colon) with an abrupt or chronically exacerbating course.
- Indeterminate (undetermined) colitis
It is an inflammation of the large intestine with characteristic overlapping features of Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis or with various atypical signs that make it impossible to clearly classify the disease.[2]
| Crohn's disease | ulcerative colitis[3][2] | |
|---|---|---|
| localization | the entire digestive tract, most often the terminal ileum | rectum and colon |
| mode of disability | segmental (alternation of inflamed and unaffected sections) | continuous progress in the oral direction |
| Abdominal X-ray | thickening of the intestinal wall, stenosis | extinct haustration |
| endoscopy | discontinuous involvement, focal aphthae, linear ulcers | hemorrhagic mucosa, diffuse inflammation, pseudopolyps |
| histology | inflammation of all layers of the intestinal wall (transmural) | inflammation of the mucous membrane and submucosa |
| typical epithelioid granulomas, lymphocytic infiltrates | cryptitis, crypt abscesses | |
| clinical picture | abdominal pain, diarrhea - rarely with blood | bloody diarrhea with tenesmus |
| fever, weight loss, anorexia, growth retardation | ||
| complications | formation of fistulas, stenoses and abscesses | increased risk of cancer |
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- ZÁDOROVÁ, Zdena. Czech Gastroenterological Society : Nonspecific intestinal inflammation [online]. ©2007. [cit. 2010-05-02]. <https://www.cgs-cls.cz/informace-pro-pacienty/nespecificke-strevni-zanety/>.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ ŠERCLOVÁ, Z. Recommended procedures for surgical treatment of patients with non-specific intestinal inflammation - Part 1: preoperative preparation [online]. ©2015. [cit. 2019-06-07]. <https://www.cgs-cls.cz/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/06.pdf>.
- ↑ a b c LEBL, J – JANDA, J – POHUNEK, P. Clinical Pediatrics. 1. edition. Galen, 2012. 698 pp. pp. 311-318. ISBN 978-80-7262-772-1.
- ↑ MUNTAU,. Pediatrics. 4. edition. Grada, 2009. pp. 372- 377. ISBN 978-80-247-2525-3.