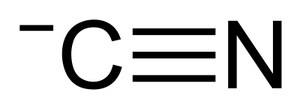
Hydrogen cyanide and cyanide intoxication
Hydrogen cyanide (HCN), potassium cyanide (KCN), sodium cyanide (NaCN) is one of the fastest acting and most violent poisons . Lethal dose : 1 mg/kg of weight. Gas can be felt after the bitter tonsils (this ability is genetically determined, not everyone feels it). It is slightly lighter than air. It was used by the Nazis in gas chambers (the so-called Zyklon B ).
The salts are also highly lethal, the lethal dose of KCN (cyankali) is 100-250 mg (on the tip of a knife). The toxicity of the salts decreases over time , as they turn into carbonates thanks to the CO 2 in the air.
Professional exposure[edit | edit source]
Exposure to salts in galvanizing plants – use for plating (gold plating, silver plating, copper plating), extraction of gold and silver from ores... When salts come into contact with acid, HCN is released, it is also released when burning – especially plastics with nitrogen in the molecule (polyurethanes. .). It is also produced from bitter almonds (after glucose is split off from amygdalin – the lethal dose is about 30 pieces). Another source is organic cyanides - eg sodium nitroprusside (medicine for hypertensive crisis).
Etiopathogenesis[edit | edit source]
It causes a blockage of cellular respiration by binding to Fe 3+ in cytochrome oxidase in the mitochondria . Inhibition of cytochrome oxidase causes interruption of oxidative phosphorylation , lactate rises and metabolic acidosis occurs . Venous blood becomes arterialized (has a lot of oxygen) and is lighter red.
The cyanide organism detoxifies hepatic thiosulfate by sulfotransferase (rhodanase) to SCN, which is excreted in the urine. The gas is absorbed very quickly and can cause sudden death . After ingestion of salt, HCN is produced in the stomach by the action of HCl, the onset of effects is slower, it depends on the acidity in the stomach, the age of the salt, and the amount of food.
Clinical picture[edit | edit source]
After inhalation of HCN: dizziness , confusion , convulsions , vomiting , tachycardia , unconsciousness , death by respiratory arrest.
After ingestion of salt, the symptoms develop within tens of minutes, the breath smells like "bitter almonds".
Diagnosis[edit | edit source]
ABB : metabolic acidosis (MAc), saturation is sufficient, it is increased in the veins.
Differential diagnosis[edit | edit source]
It is necessary to distinguish other intoxications - CO and carbon disulfide .
Therapy[edit | edit source]
- First, the victim must be removed from the HCN-contaminated environment.
- When he is not breathing - controlled breathing during inhalation can lead to intoxication of the rescuer.
- If a person is fine after inhalation, we can assume that it will be fine, after oral we have to take into account the latency.
Traditional therapy – HCN has an affinity mainly for Fe 3+ , so it does not bind to classic hemoglobin , but it binds well to methemoglobin, so methemoglobinemia is induced with the help of oxidizing agents (4-dimethylaminophenol, nitrates) ; this method has its risks, but it has a quick effect.
A new method of therapy – binding to hydroxycobalamin (from vitamin B12 ), the treatment is risk-free, but expensive.
- I. degree of therapy
- Inhalation of amylium nitrosum (Amyl nitrite) from a broken glass tube,
- will make 5% methemoglobinemia, this help is also provided by a layman,
- hydroxycobalamin inj. 4–10 g IV
- II. degree of therapy
- Sodium thiosulfate inj. 4–12 g IV ,
- does not have severe NU, the effect is slower.
Links[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- BENEŠ, Jiří. Studijní materiály [online]. [cit. 24.02.2010]. <http://jirben.wz.cz>.
References[edit | edit source]
- PELCLOVÁ, Daniela. Nemoci z povolání a intoxikace. 2. edition. Karolinum, 2006. 207 pp. ISBN 80-246-1183-X.