Genealogy
Genealogy is the study of genealogy; serves for basic research on the genetic regularities of transmission of a certain trait and for practical application in the field of counseling in clinical genetics.
In a broader sense, genealogy is a branch that deals with lineage relationships between individuals of a certain species. The name genealogy is a combination of two Greek words: genea = origin/lineage and logos = knowledge.
A person examines family connections (kinship relationships), for example, when studying historical events, when following the inheritance of certain traits, etc.
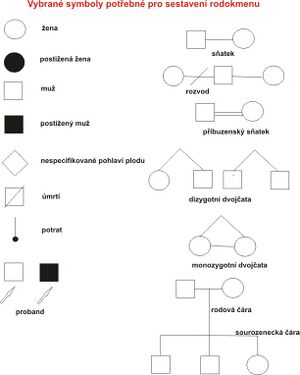
From a biological point of view, genealogy is considered as one of the methods of genetic research. In this case, the basis of the genealogical method is the graphic recording of genealogical relationships between individuals in individual generations; i.e. creating a family tree. The compilation of a pedigree and a written record (legend) that provides more detailed information about the family is done by a clinical geneticist (see also family history). The family tree graphically captures basic information about the occurrence of the selected character. In the family tree, a person who provides information for the creation of a family tree study and is interested in evaluating the probability of character repetition (proband) is marked with an arrow. Standard symbols are used when constructing a family tree graphically (see diagram).
Genealogical Analysis[edit | edit source]
To investigate the type of genetic determination, a number of statistical methods have been developed that enable detection of cleavage ratios, penetrance of the monitored gene and estimates of heritability:
- For highly polymorphic characters, a random selection from the set of all families of the given population.
- For rare traits, selection of families, when in the case of a dominant trait, selection can be made through an affected parent.
- In the material collected in this way, the cleavage ratios in the offspring can be examined by simple calculation.
- In the case of AR rare traits, most of the parents are clinically healthy (Aa), we select only those families where at least one affected child was born.
Research Genealogy Method[edit | edit source]
It consists in principle in the selection of families where the appropriate type of crossing has occurred. The person who led to the selection of a particular family is referred to as the proband. The families are then examined by an expert from the examination record. From the record, a graphic representation is made in the form of a genealogical scheme, a family tree, for the compilation of which standardized marks are used.
One, at most a few characters can be captured graphically in the scheme so that the visuality of this method is not violated. Additional information found should be recorded in the legend of the family tree. The data obtained must be as deep as possible (to the most distant ancestors) and as broad as possible (including distant relatives).
The obtained genealogical material is subsequently subjected to logical analyses. We try to explain the transmission of characters in individual families using letter schemes used in experimental phenogenetics.