Gamma-glutamyl transferase
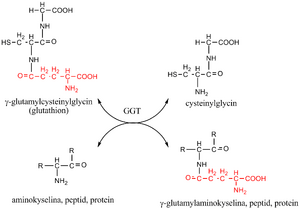
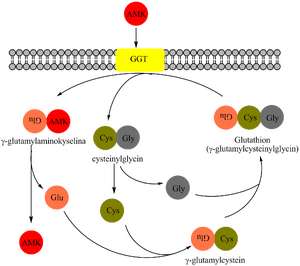
γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT, formerly also GMT, EC 2.3.2.2) is a key enzyme of the γ-glutamyl cycle, which ensures the transport of some aminoacids and peptides across the cell membrane from the extracellular fluid into the cells.
GGT catalyzes the transfer of the γ-glutamyl group: from γ-glutamyl peptides to other peptides, amino acids or water. The donor of the γ-glutamyl residue is the tripeptide glutathione (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) found in the cells of animals, plants and bacteria. It protects the organism from oxidative stress (participates in the removal of hydrogen peroxide). It is regenerated by a reaction catalyzed by glutathione reductase.
Occurrence of GGT[edit | edit source]
Membranes of cells with high secretory or absorptive capacity, liver (microsomal fraction of hepatocytes and bile ducts lining cell membranes), proximal tubules of the kidneys, enterocytes and pancreas.
GGT synthesis is also induced by some drugs (barbiturates, antidepressants, alcohol). It can also be released from membranes by the action of detergents, e.g. bile acids or alcohol.
Evaluation of GGT activity in serum[edit | edit source]
An increase in GGT activity is typical mainly for damage to the hepatobiliary tract. This occurs with intrahepatic or extrahepatic cholestasis (in these cases alkaline phosphatase), is also increased ), hepatocellular damage – acute and chronic liver diseases, liver and pancreatic tumors.
A high isolated increase in GGT may be a sign of liver damage due to chronic alcohol consumption. There is increased activity in alcoholics even if the liver is not yet damaged (induction of GGT synthesis).
Determination of GGT[edit | edit source]
The determination principle is based on the reaction that GGT catalyzes physiologically in the body. The transfer of the γ-glutamyl residue from the substrate to the acceptor, which is glycylglycine, is monitored. L-γ-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide or L-γ-glutamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide are used as substrates. During the reaction, after the transfer of the γ-glutamyl residue to the acceptor, colored p-nitroaniline (from the substrate of L-γ-glutamyl-p-nitroanilide) or 5-amino-2-nitrobenzoate (from the substrate of L-γ-glutamyl-3-carboxy-4-nitroanilide), the increase of which is directly proportional to the activity of GGT in the examined sample.
| Physiological levels of fS-GGT | |
|---|---|
| Male | 0,14–0,84 μkat/l |
| Female | d0,14–0,68 μkat/l |
Physiologically, GGT values are higher in men, due to the higher content in the prostate.