COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT)
From WikiLectures
- Previous chapter: 6.3 X-RAY
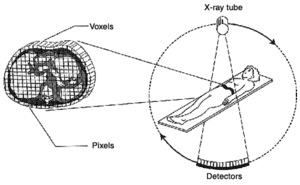
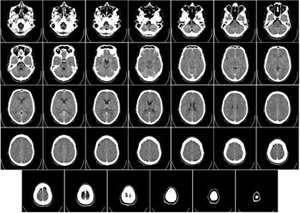
X-ray computed tomography, also computed tomography (CT scan), is a medical imaging procedure that utilizes computer-processed X-rays to produce tomographic images or 'slices' of specific areas of the body. These cross-sectional images are used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in various medical disciplines.
This method simply uses a simple X-ray with detector on the other side but it is mounted on support that is able to rotate around the patient and produce many cross-sectional slices. These slices are next processed using mathematical modeling to produce a 3D image.
- Next chapter: 6.5 SINGLE-PHOTON EMISSION COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (SPECT)
- Back to Contents