Ménière's disease
Ménière's disease is a disease of the inner ear arising from dysfunction of the endolymphatic sac . Women and men are affected equally. The disease occurs mainly in patients aged 30–60 years.
Pathogenesis[edit | edit source]
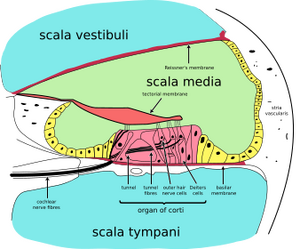
Saccus endolymphaticus ensures the resorption of endolymph. Its dysfunction results in the accumulation of endolymph and expansion of the labyrinth, leading to its rupture. Endolymph is rich in potassium and therefore diffuses into the potassium-poor perilymphatic fluid. This leads to depolarization of the vestibulocochlearis neuron .
Clinical signs[edit | edit source]
The main symptoms of Ménière's disease include:
- Paroxysmal vertigo – these are bouts of rotational vertigo, often preceded by an aura.
- Tinnitus – typically unilateral.
- Hypacusis – typically one-sided perceptual.
There are also frequent feelings of pressure in the ear, nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostics[edit | edit source]
Ménière's disease can be diagnosed based on:
- anamnesis (two or more past vertigo attacks);
- audiometry (we demonstrate a shift in hearing threshold by more than 10 dB at two different frequencies);
- exclusion of other pathological conditions that could lead to a similar clinical manifestation (indicated methods may include e.g. CT , MRI , lumbar puncture, angiography...).
Treatment[edit | edit source]
The causal treatment for Ménière's disease is unknown . They are used:
- special dietary measures – limit salt, limit intake of caffeine, alcohol;
- diuretics ;
- betahistin.
In case of failure of conservative therapy, surgery can be performed (on the saccus endolymphaticus).
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- BENEŠ, Jiří. Studijní materiály [online]. ©2007. [cit. 2009]. <http://jirben2.chytrak.cz/materialy/orl_jb.doc>.
References[edit | edit source]
- KLOZAR, Jan, et al. Speciální otorinolaryngologie. 1. edition. Praha : Galén, 2005. 224 pp. ISBN 80-7262-346-X.
- MLČOCH, Zbyněk. Menierova nemoc, Menierův syndrom – příznaky, projevy, léčba, diagnostika, vyšetření [online]. ©c2003-2010. [cit. 2017-10-12]. <http://www.zbynekmlcoch.cz/informace/medicina/nemoci-lecba/menierova-nemoc-menieruv-syndrom-priznaky-projevy-lecba-diagnostika-vysetreni>.
- Vertigo Academy. Endolymfatický hydrops : Ménièrova choroba a Ménièrův syndrom [online]. [cit. 2010-05-20]. <http://www.vertigoacademy.cz/zavrat/priciny>.