Limb development
Embryonic Resources[edit | edit source]
Mesenchyme – the skeleton and connective tissues of the limb.
Immigrated cells – myogenic cells, melanoblasts , Schwann cells , angioblasts .
Ectoderm - epidermis , apical ectoderm strip.
Week 4[edit | edit source]
At the end of the fourth week, limb buds and outgrowths appear on the ventrolateral side of the body of the embryo . Limb buds are formed by a mesenchymal core that is covered by ectoderm. The mesenchymal nucleus is originally from the somatopleura of the lateral mesoderm . Cells of other tissues migrate to the limbs. The upper limb bud appears 2 days earlier than the lower limb bud. In the entire development of the limbs, the development of the lower limbs is a little behind the development of the upper limbs.
Week 5[edit | edit source]
The upper limb buds are paddle-shaped. The lower limb buds take the shape of fins.
Week 6[edit | edit source]
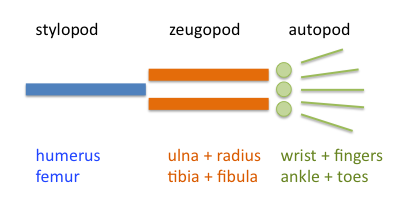
In the sixth week, the distal part of the limb flattens and forms the base of the hand and foot, i.e. the autopodium separated by a circular constriction from the rest of the limb, i.e. the axopodia . Later, the axopodium divides by a similar circular constriction into the stylopodium (thigh) and the zeugopodium (calf). In the sixth week, the mesenchymal cells also begin to thicken, multiply and differentiate into chondrocytes . Chondrocytes create the first cartilaginous models of future bones. Fingers are also starting to form - the so-called digital rays. In the sixth week, limb movements can also occur.
Week 7[edit | edit source]
During the seventh week, the limbs rotate, the upper limbs outward, i.e. the extensor side dorsally with the thumb laterally, and the lower limbs inward, i.e. the extensor side ventrally with the thumb medially. Fingers are formed by apoptosis of cells in the future interdigital spaces.
Week 8[edit | edit source]
At the end of the embryonic period, chondrogenic ossification of limb bones begins. The formation of the fingers is already complete, but the membrane that connects the fingers still resides proximally.
Week 12[edit | edit source]
In the 12th week, primary ossification centers are formed in the diaphysis of long bones. Ossification begins in the perichondrium of the diaphysis. Immediately, vessels grow into the cartilage in the center of the diaphysis and a primary ossification center is formed.
Postnatal Development[edit | edit source]
Usually, the diaphysis is completely ossified already at birth. Secondary ossification centers are formed in the epiphyses only in the early phase of postnatal development. The only exception is the distal epiphysis of the femur , where a secondary ossification center is formed before birth. At the interface of the epiphyses and diaphysis, the epiphyseal growth plate persists, which is important for bone growth in length. The growth plate disappears when the bone reaches its final length (between 14 and 18 years of age in most bones ) and the epiphyses fuse with the diaphysis.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- MOORE, Keith L. – PERSAUD, T. V. N. Zrození člověka. 1. edition. Praha : ISV, 2002. pp. 564. ISBN 80-85866-94-3.
- SADLER, Thomas W. Langmanova lékařská embryologie. 10. edition. Praha : Grada, 2011. pp. 432. ISBN 978-80-247-2640-3.