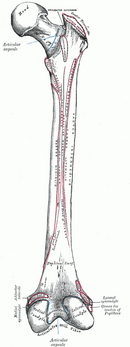
Femur
The femur (thigh bone) is the longest and strongest bone in the human body.
Main parts[edit | edit source]
- Caput femoris − head,
- collum femoris − neck,
- corpus femoris − body,
- condyli femoris − articular surfaces for connection with the tibia .
Caput femoris[edit | edit source]
The head has a diameter of around 4.5 cm. We find the joint surface on it, which corresponds to about three quarters of the surface of the ball. At the top of the head there is a hole for attaching the ligs. capitis femoris − fovea capitis femoris .
Collum femoris[edit | edit source]
The neck forms an angle of approximately 125° with the body of the femoral bone (the so-called collodiaphyseal angle). Compared to the frontal plane, the neck is turned by 10° (the so-called torsion angle).
Corpus femoris[edit | edit source]
There are two bumps at the top end:
- trochanter major (big trochanter) − extends laterocranially, serves as an attachment for the gluteus medius , gluteus minimus and piriformis muscles ,
- trochanter minor (small crest) − extends dorsomedially, serves as an attachment for the iliopsoas muscle .
The inner surface of the greater trochanter has a fossa - fossa trochanterica , which serves as an attachment for the obturatorius externus , obturatorius internus , gemellus superior and gemellus inferior .
In front, it connects both trochanters − the linea intertrochanterica , on which the ligament attaches . iliofemorale . At the back, it connects both trochanters - crista intertrochanterica , on which the quadratus femoris muscle attaches .
On the body of the femur we also find:
- tuberositas glutea − attachment for the gluteus maximus muscle ,
- linea pectinea − attachment for the pectineus muscle ,
- linea aspera − a line converging in the center of the back of the femur, made up of two lines:
- medial labium ,
- labia laterale ,
− the facies poplitea extends between them , which is distally terminated by the edge − linea intercondylaris .
At the end of the body of the femur there is a bump on both sides:
- epicondylus medialis − internal epicondyle,
- epicondylus lateralis − external epicondyle.
Condyles femoris[edit | edit source]
The surfaces of the condyles serve as articular surfaces for connection with the tibia .
- Medial condyle ,
- lateral condyle .
The fossa intercondylaris separates the two condyles at the back , the facies patellaris connects the two condyles at the front .
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- – GRIM, Miloš. Anatomie. 2. edition. Praha : Grada Publishing, 2001. 497 pp. vol. 1. ISBN 80-7169-970-5.