Follicular cyst of the maxilla and mandible - case report
From WikiLectures
This article has been translated from WikiSkripta; ready for the editor's review.
Follicular cyst[edit | edit source]
A follicular cyst arises from the epithelium of the tooth germ. It is mostly associated with the retention of the corresponding tooth. If it remains undetected, it can dislocate the surrounding teeth by gradual growth, deform the jaws and sometimes be the cause of jaw inflammation.
Case report[edit | edit source]
- A 13-year-old boy comes to the dentist for an examination before orthodontic therapy;
- during clinical examination palpable arching alveolar process loco 23 (it was retained);
- the patient had signs of facial asymmetry during the clinical examination;
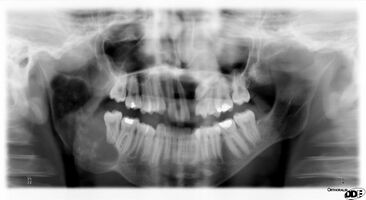
- after an orthopantomogram accidental finding of a cyst mandible loco 48 and maxilla loco 23;
- the patient underwent a high-resolution CT which confirmed the diagnosis;
- patient in general health;
- allergy to Maxitrol and mites;
- without chronic medication.
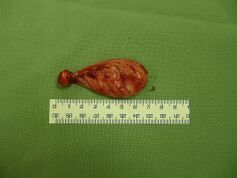
- Ordered for a surgical procedure, during which an extensive extirpation of the cyst affecting almost the entire branch of the mandible on the right was performed and the tooth germ 48 was extracted, which was pushed by the cyst to the base of the articular process of the mandible. The defect created by the extirpation was filled with bone grafts obtained from the dorsum of the iliac blade on the right. Furthermore, the area of tooth 23 was revised – the second cyst was extirpated, tooth 18 was extracted, this procedure was complicated by the formation of oro-antral communication. Tooth 23 was left to spontaneously erupt. The material was sent for histological examination.
- Histological examination confirmed dg. follicular cysts;
- after about 3 weeks, satisfacting healing process with only a small dehiscence of loco 48.