Examination of antioxidant capacity parameters
From WikiLectures
Direct measurement is difficult due to the short half-life free radicals (VR). Substances caused by their action are determined.
Direct determinations[edit | edit source]
Determination of oxygen radicals[edit | edit source]
- pulsed radiolysis - radicals are generated by ionizing radiation
- electron spin resonance spectrometry (ESR) - identification according to spin changes
- chemiluminescence method
Determination of nitrogen radicals and its adducts[edit | edit source]
- nitric oxide - very difficult to determine
- methods such as oxygen
- most often indirect methods - nitrites, nitrates or substances modified by nitration - nitrosohemoglobin
Determination of radical generating substances[edit | edit source]
- xanthine oxidase - produces superoxide
- determination of transition metals - Fe, Cu (catalyses reactions where free radicals are formed)
Indirect measurements[edit | edit source]
- most often determination of lipoperoxidation products, adducts with DNA
VR Damage Products[edit | edit source]
Damage to NK[edit | edit source]
- the most significant (irreversible) damage - hydroxyl radical
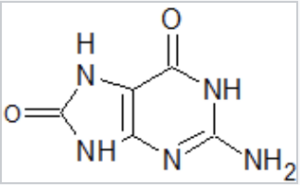
- main product - thymine glycol and 8-hydroxyguanine
- repair enzymes remove them from cells - we can determine them in the urine
Damage to proteins and AMK[edit | edit source]
- many damage mechanisms, little used
- a sensitive method is for measuring carbonyl residues from lysine
Lipoperoxidation[edit | edit source]
- in direct connection with the formation of free radicals
- most common - determination of malondialdehyde (MDA) - reaction with thiobarbiturate forms a color complex, non-specific, also reacts eg bilirubin, DNA
- also other aldehydes (eg 4-hydroxynonenal)
- conjugated dienes - characteristic UV absorption (234 nm)
- measurement of hydrocarbons in exhaled air
- isoprostanes - by peroxidation product ofarachidonic acid
Oxidized LDL[edit | edit source]
- contribution to atherosclerosis
- 2 methods
- delayed phase change during stimulated peroxidation - examines the ability of LDL to cope with oxidative stress
- determination of oxLDL - extraction, oxFFA is determined at 234 nm
Antioxidant protection of the organism[edit | edit source]
Total antioxidant capacity[edit | edit source]
- artificial formation of free radicals in biological material - we measure the ability to slow down or stop this reaction
- TRAP determination - ability of plasma after the addition of a generator - conversion to the Trolox capacity - 1 molecule of trolox has 2.0 units when using TRAP - disadvantage - end-point oxygen electrode
- more used ABTS - inhibition of ABTS radical cation
Antioxidant enzymes[edit | edit source]
- determination of SOD rather indirectly, determination of catalase - rarely
Antioxidant substrates[edit | edit source]
- vitamins A, E, C
- determination of thiols is irrelevant (they are on albumin, they have a long half-life)
- also others - ubiquinone Q, lipoate, flavonoids…, using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)