Diagnostic imaging methods in senology
Mammology = diagnosis and treatment of breast diseases.
Mammography (MMG)[edit | edit source]
Mammography is a skiagraphic examination of the breast. According to the indication, it is divided into:
- Screening (also screening) - as part of the screening examination of women without symptoms (asymptomatic women),
- Diagnostic - palpation finding, other suspicion of breast tumor.
Soft x-ray radiation (with lower energy) is used, 2 projections - (oblique and craniocaudal), nowadays mostly digital.
Advantages of digital mammography:
- enables the application of lower doses of radiation,
- additional editing of images,
- remote sending (ePACS),
- archiving in digital form,
- image evaluation by computer − Computer Aided Detection − CAD.
| Mamografie: tukový typ, Tabár 2 |
Screening mammography[edit | edit source]
Screening mammography is an examination of healthy women from a certain age with the aim of detecting as many non-palpable small tumors with a good prognosis as possible, over 10% are non-invasive carcinomas. In the Czech Republic, the screening examination is covered by the insurance company from the age of 45 once every 2 years and only in accredited centers; when using HRT it is suitable once a year, with increased risk (BRCA, family history) already at a younger age and more often.
Ductography[edit | edit source]
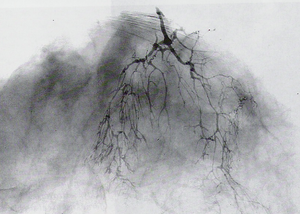
Ductography is indicated for unilateral massive serous or bloody secretion from the breast. An injection of contrast substance is performed with a cannula into the secreting duct and then MMG. Used to look for intraductal lesions - usually papillomas or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
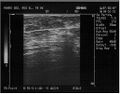
Ultrasonography (US)[edit | edit source]
Cysts, fibroadenomas, inconclusive findings in MMG, in older age as auxiliary examination, primarily in younger women, during pregnancy, during lactation, for examination drainage nodes and postoperative monitoring of the scar. Due to the inability to detect microcalcifications, it is not suitable for screening. It is often used in the navigation of biopsy examinations (FNAB, core-cut biopsy).
| US prsu: karcinom |
| US prsu: kalcifikace |
| US prsu: fibroadenom |
| US prsu: prsní implantát |
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR mammography)[edit | edit source]
Ambiguous findings, puncture finding of lobular carcinoma or carcinoma in the dense breast to rule out multifocality or bilaterality, in post-operative patients to differentiate between scar and new carcinoma, search for primary carcinoma when nodes in the axilla are affected, screening method in high-risk women (together with US and later also with MMG), use of a special (so-called breast) coil.
Core-cut biopsy[edit | edit source]
Percutaneous tissue collection with a special 14G needle with biopsy cannon, outpatient procedure - local anesthesia, skin incision, collection of several samples, mostly US navigation (under sonographic control), indications for ambiguous or from from the point of view of cancer, positive findings on MMG and/or US, verification of obvious cancers before treatment, enables the individualization of breast cancer treatment (often replaces peroperative biopsy), allows determining the histological type, grade and other prognostic factors, including immunohistochemical examinations.

|
US prsu: biopsie ložiska |
Mammotomy − vacuum biopsy[edit | edit source]
Special device and needle (11G) with rotary knife for percutaneous tissue sampling, larger volume of sampled tissue, mostly navigation by mammographic stereotaxic, main indication for ambiguous microcalcifications, disadvantage is higher invasiveness and price of one sample (about 15 thousand CZK).
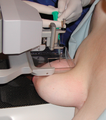
Mammographic stereotaxy[edit | edit source]
Procedure for localization or biopsy of a non-palpable mass in the breast that is not visible with US, special mammography equipment, digital detector, two projections ±15° calculation coordinate x,y,z, exact localization about 1−2 mm, indication of particularly ambiguous microcalcification.
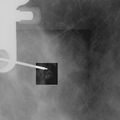
Percutaneous localization of deposits in the breast[edit | edit source]
Localization wires, color (carbo adsorbent suspension), X-ray contrast clips, pre-operative for the surgeon, cancer marking before neoadjuvant therapy.
![]() Approx 10−15 % of palpable breast cancers(resistance or nodules) do not have a convincing correlation with MMG - supplement US and comparison with palpation findings necessary!
Approx 10−15 % of palpable breast cancers(resistance or nodules) do not have a convincing correlation with MMG - supplement US and comparison with palpation findings necessary!
Diagnostics is mainly concentrated in accredited screening centers, where complex diagnostics, all main methods, extensive experience, quality equipment, regular check-ups, diagnosis of breast diseases are primarily provided by a radiologist - mammodiagnostic, close teamwork with a gynecologist, surgeon, oncologist, radiotherapist, pathologist, etc. necessary!
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- Images at atlas.mudr.org
- Teaching portal of the 1st Faculty of Medicine, UK – Radiodiagnostics: Quiz: imaging methods in senology, gynecology and obstetrics
- Screening program of the Czech Republic: www.mamo.cz
- Tabarova typology at www.mudr.org