Detection of antibodies against gliadin, endomysium and atTG in stool
From WikiLectures
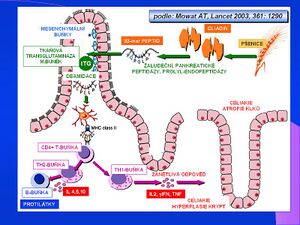
Testing a stool sample is beneficial for screening programmes in gastroenterology. Determination of secretory IgA antibodies to gliadin is another new immunochemical test, commercially available since 2000, that can be used in the screening of celiac disease. The test is based on ILMA (ImmunoLuminoMetric Assay) principle with luminescence measurement, the marker is acridinium ester, and the antigen is raw gliadin. The test determines the prescence of secretory IgA antibodies - anti-gliadine-scIgA, normal values are up to 100 mg/g of stool, and clinical sensitivity is 81%, specificity is 97%. There is also a new ELISA detection of IgA antibodies to endomysium and fecal transglutaminase.
References[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- with permission of the author taken from KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedie laboratorních metod v gastroenterologii [online]. ©2002. Poslední revize 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
Literature[edit | edit source]
- KAPPLER, M, et al. Detection of secretory IgA antibodies against gliadin and human tissue transglutaminase in stool to screen for coeliac disease in children: validation study. BMJ. 2006, vol. 332, no. 7535, s. 213-4, ISSN 0959-8138 (Print), 1468-5833 (Electronic). PMID: 16377644.
- HALBLAUB, JM, et al. Comparison of different salivary and fecal antibodies for the diagnosis of celiac disease. Clin Lab. 2004, vol. 50, no. 9-10, s. 551-7, ISSN 1433-6510. PMID: 15481630.
- PICARELLI, A, et al. Antiendomysial antibody detection in fecal supernatants: in vivo proof that small bowel mucosa is the site of antiendomysial antibody production. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002, vol. 97, no. 1, s. 95-8, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 11808976.