Somatic and gametic chromosomal aberrations
From WikiLectures
Chromosomal aberrations are numerical or structural deviations from the normal sturcture of the karytoype.
Somatic chromosomal aberrations[edit | edit source]
- it is not passed on to offspring
- in the early stages of the development of the zygote - a mosaic occurs, syndromes similar to gametic chromosomal aberrations occur
- postnatally, they usually mean the formation of tumors
- numerical and structural aberrations
- for example, the Philadelphia chromosome – t(9;22) in CML, translocation t(8;14) in Burkitt's lymphoma, etc.
Gametic chromosomal aberrations[edit | edit source]
- it is passed on to offspring
- numerical
- nondisjunction in meiosis I results in a gamete with 2 different (one from the father, one from the mother) or none of the pair of chromosomes in which the nondisjunction took place
- nondisjunction in meiosis II results in a gamete with 2 identical (both from the father or the mother) or none of the pairs of chromosomes in which nondisjunction occurred
- polyploidy – it is the multiplication of entire sets of chromosomes, genomic aberrations (hydatiform moles arise, incompatible with life)
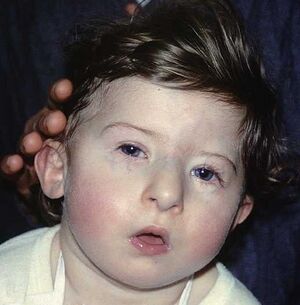
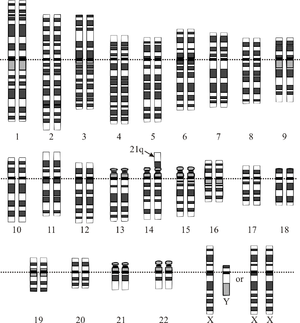
- aneuploidy – trisomy (Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, XXX syndrome, XYY syndrome) or monosomy (Turner's syndrome)
- structural
- deletion (deletion syndromes: Cri du chat syndrome (5th chromosome), deletion form of Turner syndrome; microdeletion syndromes: Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome (4th chromosome), Prader-Willi and Angelman syndrome (15th chromosome), DiGeorge syndrome , etc.) – terminal and interstitial deletion
- duplication
- insertion
- inversion
- ring chromosome
- chromosome marker
- dicentric chromosome
- translocation – reciprocal and Robertsonian
- isochromosome
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- OTOVA, Berta, et al. Medical biology and genetics I. vol. 1st edition. Prague: Karolinum, 2008. 123 pp. ISBN 978-80-246-1594-3 .