Integral and selective detection of gamma radiation
Amplitude Analyzer[edit | edit source]
The amplitude analyzer is currently an important step to the processing of electrical impulses that are generated in the scintillation detector by registering γ-rays. The value of the electrical impulses depends on the electrical voltage of the impulse, which is sensed by the anode of the photomultiplier. This value is directly proportional to the luminescence intensity in the crystal (mostly NaI/Ta) and the radiation energy γ, that is absorbed in the scintillation detector. The detector not only captures the rays emitted by the radionuclide that accumulates in the observed organ, but also captures the rays of other energies. (cosmic radiation), natural radioactivity of the environment) could distort the measurement results and that is why an amplitude analyzer is used. Using the amplitude analyzer, we can set any value of pulses (voltage) that will be detected and others with a higher or lower value will be retained. The task of the amplitude analyzer is therefore to pass from the entire spectrum of γ radiation only rays of the selected energy. Based on this procedure, it is then possible to evaluate impulses in two ways.
Integral detection[edit | edit source]
In integral detection registered using a pulse counter or integrator , all pulses corresponding to higher amplitudes than the selected discrimination value are . Based on the so-called discrimination level, this method corresponds to integral amplitude discrimination . The area bounded by the energy axis and the curve expressing the number of pulses is proportional to the total number of detected pulses.
Selective detection[edit | edit source]
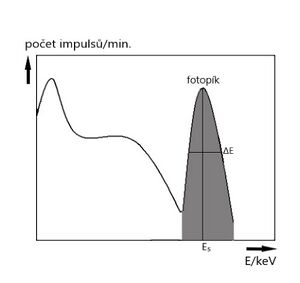
Selective detection is used to register those impulses that correspond to value in the range of the selected lower and upper discrimination values . Therefore, only impulse values in the given energy range are detected . The use of selective detection ( photopeak detection method ) corresponds to the differential amplitude discrimination . The total number of registered pulses is defined by a photopeak.
The energy resolution R expresses the properties of the scintillation detector. It is given by the relation:
where ΔE is the width of the photopeak measured at half its height and E s is the mean energy of the channel. Energy resolution is given as a percentage.
If we have a radionuclide by detecting it in the photopeak (with a suitable choice of energy and width of the photopeak) composed of several isotopes, we can measure the radiation of only one radioisotope . This applies if the given isotopes emit γ radiation of sufficiently different energy. Then there is no overlapping of their photopeaks.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- BENEŠ, Jiří. Základy lékařské biofyziky. - edition. Karolinum, 2007. 201 pp. ISBN 9788024613864.
- NAVRÁTIL, Leoš. Medicínska biofyzika. - edition. Grada, 2005. 524 pp. ISBN 9788024711522.