Enterococcus
From WikiLectures
Enterococci form the natural microflora in the intestine and vagina. They are very resistant to high pH (8.5) and temperatures. They are highly resistant to antibiotics.
- Morphology: G + cocci in pairs or chains.
- Occurrence: part of the natural microflora in the human gut.
- Cultivation: not demanding on cultivation.
- Collection of material: for diagnosis, clinical material is collected from gynecological swabs, urine or blood culture.
Diseases[edit | edit source]
Enterococci are among the conditional pathogens. They cause urinary and biliary tract infections, gynecological inflammations, postoperative complications in abdominal surgery and are involved in the development of infectious endocarditis.
Therapy: antibiotics, resistance increases especially in nosocomial strains.
Diagnostic procedure[edit | edit source]
- Material
Swabs, urine, blood culture.
- Identification
- Microscopy: G+ cocci.
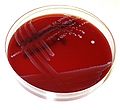
- Cultivation: BA - gray colonies (possibility of α, β or γ hemolysis), SB - violet-brown colonies.
- Tests: negative catalase test .
- Serological methods
Wall antigen detection (group D).
Representatives[edit | edit source]
Enterococcus durans, Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium
Photo gallery[edit | edit source]
Summary video[edit | edit source]
<mediaplayer width='450' height='250' >https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4rZ_bMY_oPk</mediaplayer>
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
Použitá literatura[edit | edit source]
- BEDNÁŘ, M – FRAŇKOVÁ, V – SCHINDLER, J. Lékařská mikrobiologie – bakteriologie, virologie, parazitologie. 1. edition. Praha : Marvil, 1996. 558 pp. ISBN 80-238-0297-6.
- RYŠKOVÁ, Olga. Mikrobiologie pro studující zubního lékařství. 1. edition. V Praze : Karolinum, 2004. ISBN 80-246-0834-0.
- ŠMÍROVÁ, Václava. Úvod do lékařské mikrobiologie. - edition. -.