C-13 sodium octanoate breath test
In the differential diagnostics of functional dyspepsia, reflux disease and for the indication of some modern drugs (prokinetics) the speed of emptying the stomach and motility can be used to measured by a non-radioactive and non-invasive breath test. The 13 C-octanoic acid (caprylic acid) breath test is a non-invasive gastric evacuation test.
Octanoic acid is not absorbed in the stomach, but is relatively quickly absorbed by the duodenal mucosa. The liver then produces 13 CO2, which is determined in exhaled air.
Examination of the gastric passage by a 13 C-octanoate breath test shows a high correlation with the scintigraphic method. The 13 C-octanoic acid breath test determines the amount of food that passes into the duodenum, while scintigraphy determines the amount of food that remains in the stomach. Another variantion is a13 C-acetate breath test.
Implementation[edit | edit source]
The testing breakfast can be solid (poached egg with 3 g of oil, toast - 40 g and butter 10 g) or semi-solid (200 g of milk, chocolate pudding). 100 mg of sodium 13 C-octanoic acid is added to the testing breakfast. The sampling of the exhaled air is performed continuously for 4 hours. The evaluation of the process kinetics by measuring the change in the ratio of 13 CO 2 : 12 CO 2 can be performed by IRMS or IR analyzers.
The normal range is 110-160 minutes for a solid diet and 91-155 minutes for a semi-solid diet.
Links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- SANAKA, M. The Wagner-Nelson method makes the [13C]-breath test comparable to radioscintigraphy in measuring gastric emptying of a solid/liquid mixed meal in humans. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007, vol. 34, no. 7, p. 641-4, ISSN 0305-1870 (Print), 1440-1681 (Electronic). PMID: 17581222.
- HAUSER, B. Variability of the 13C-octanoic acid breath test for gastric emptying of solids in healthy children. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006, vol. 23, no. 9, p. 1315-9, ISSN 0269-2813 (Print), 1365-2036 (Electronic). PMID: 16629936.
- BLUCK, LJ. Measurement of gastric emptying by the 13C-octanoate breath test--rationalization with scintigraphy. Physiol Meas. 2006, vol. 27, no. 3, p. 279-89, ISSN 0967-3334 (Print), 1361-6579 (Electronic). PMID: 16462014.
- BURES, J. Examination of gastric emptying rate by means of 13C-octanoic acid breath test. Methods of the test for adults and results of the investigation of healthy volunteers. Cas Lek Cesk. 2005, vol. 144, no. Suppl 3, p. 18-22, ISSN 0008-7335 (Print). PMID: 16335258.
- YAMAMOTO, T. Modified 13C-octanoate breath test and impact of sampling points. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2004, vol. 38, no. 8, p. 669-70, ISSN 0192-0790 (Print), 1539-2031 (Electronic). PMID: 15319649.
- CHEN, CP. Infrared spectrometry based 13C-octanoic acid breath test in measuring human solid gastric emptying. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 41-6, ISSN 0815-9319 (Print), 1440-1746 (Electronic). PMID: 12519222.
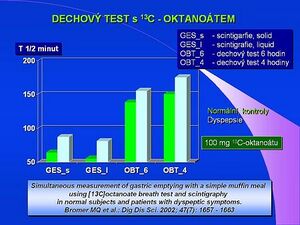
- BROMER, MQ. Simultaneous measurement of gastric emptying with a simple muffin meal using [13C]octanoate breath test and scintigraphy in normal subjects and patients with dyspeptic symptoms. Dig Dis Sci. 2002, vol. 47, no. 7, p. 1657-63, ISSN 0163-2116 (Print), 1573-2568 (Electronic). PMID: 12141833.
- KULIK, W. Improved use of the [13C]octanoic acid breath test as intra-individual parameter to study the effect of a prokinetic drug on gastric emptying in preterm infants with oral feeding intolerance. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 2001, vol. 750, no. 1, p. 147-53, ISSN 1387-2273 (Print). PMID: 11204215.
- CHEY, WD. Gastric emptying characteristics of a novel (13)C-octanoate-labeled muffin meal. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001, vol. 32, no. 5, p. 394-9, ISSN 0192-0790 (Print), 1539-2031 (Electronic). PMID: 11319309.
- CAPPELLO, G. Gastric emptying of a solid-liquid meal measured with 13C octanoic acid breath test and real-time ultrasonography: a comparative study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000, vol. 95, no. 11, p. 3097-100, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 11095323.