Bronchus (histology)
Sample 1[edit | edit source]
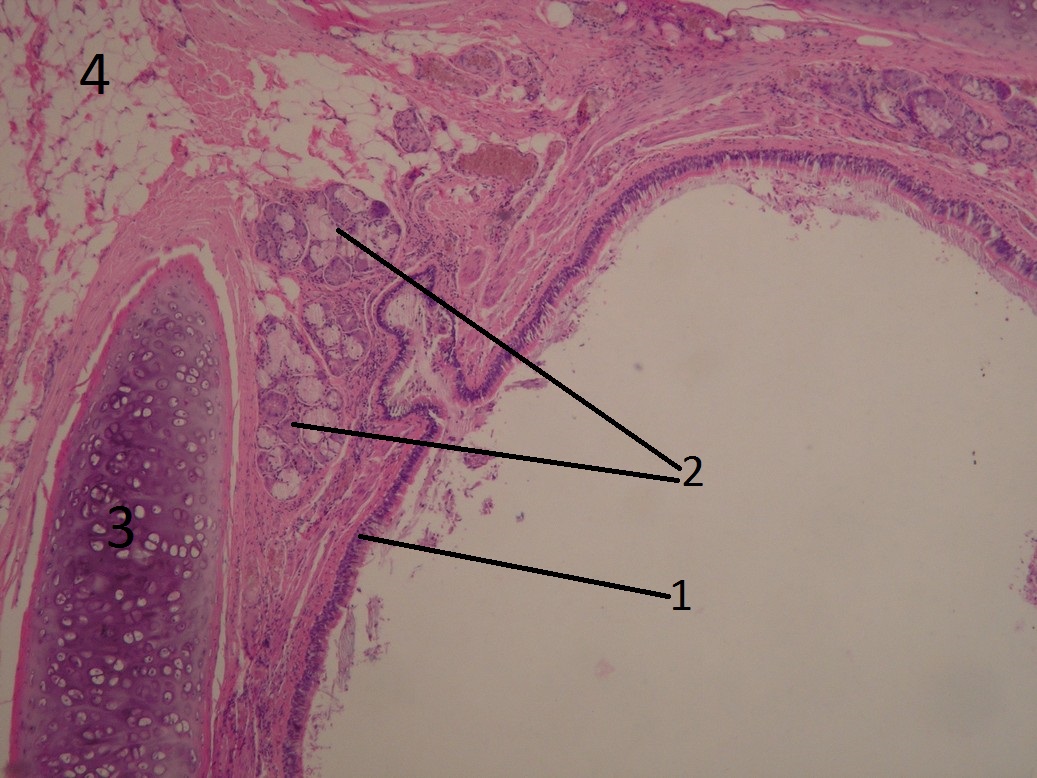
Name: Bronchus - low magnification (HE)
Description: The bronchus is lined by a multi-rowed columnar epithelium with cilia. Underneath it is a thin collagenous lamina propria mucosae. In the wall we see hyaline cartilage (tunica fibro-musculo-cartilaginea) and sero-mucinous glands.
1 - lamina epithelialis 2 - sero-mucinous glands 3 - cartilage 4 - fatty tissue
Sample 2[edit | edit source]
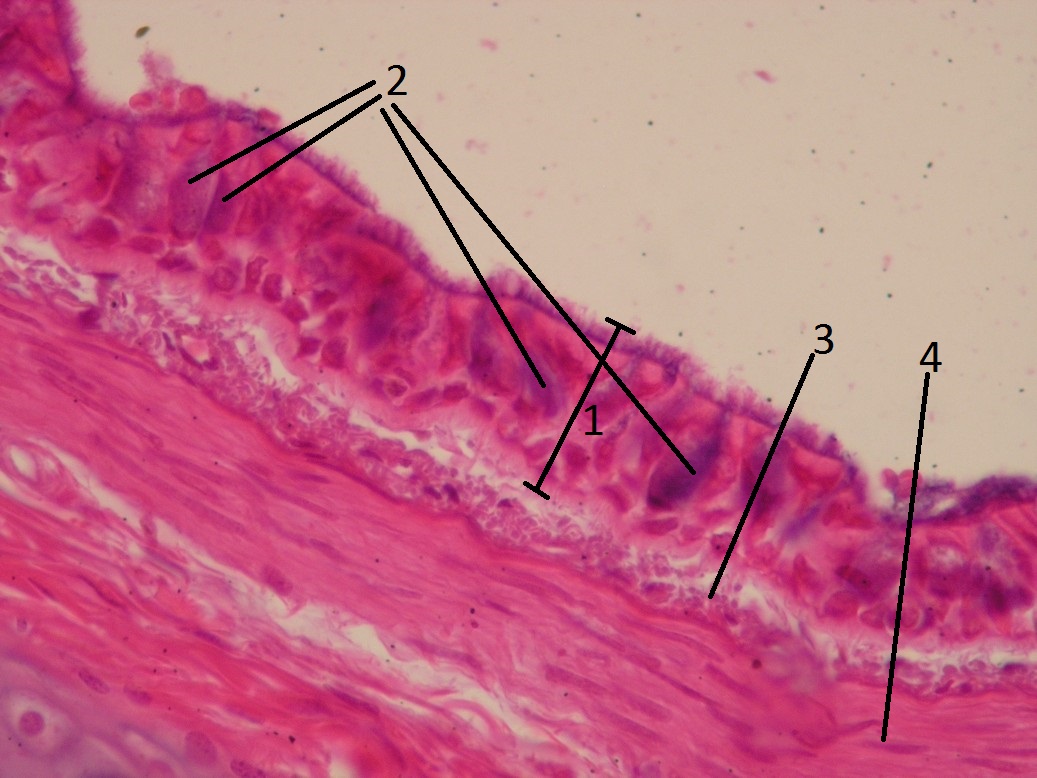
Name: Multi-rowed cylindrical epithelium with cilia (Bronchus); (HE)
Description: In stratified epithelium, all cells reach the basal lamina, but their nuclei are located at different heights. It appears as if the cells form layers. Epithelium contains ciliated cells, basal cells, goblet cells, and brush border cells. The mucin in the goblet cell is stained blue. Note: Mucin is usually washed out during fixation, which is why vacuoles are usually seen as white (bright spots). With this preparation, it was possible to fix the mucin (make it insoluble). As an acidic structure (glycoprotein), it stains basophilic.
1 - the entire thickness of the epithelium 2 - goblet cells 3 - lamina propria 4 - tunica fibro-musculo-cartilaginea (here denser connective tissue and smooth muscle cells)
Sample 3[edit | edit source]
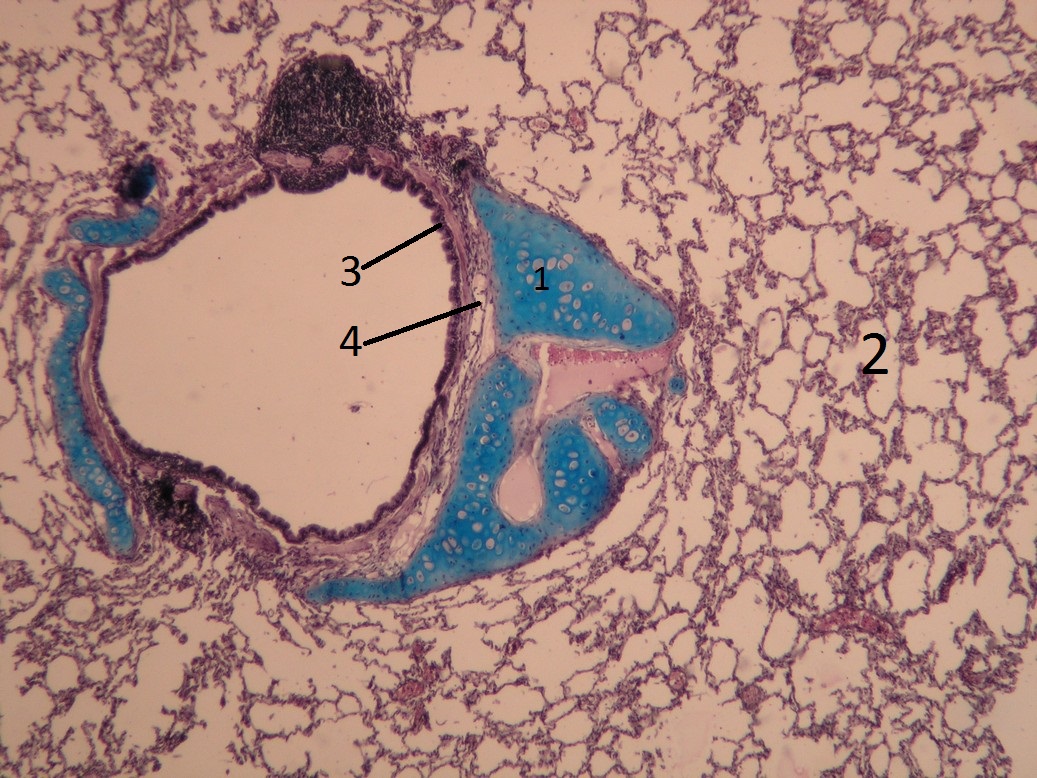
Name: Intrapulmonary bronchus (staining - Alcian blue, hematoxylin)
Description: The hyaline cartilage in the bronchus is colored blue. A lymph node (follicle) can be seen in the wall above. The bronchus is surrounded by lung tissue (single-layered squamous epithelium).
1 - cartilage, 2 - pulmonary alveoli, 3 - respiratory epithelium (multi-row cylindrical epithelium with cilia) 4 - tunica fibro-musculo-cartilaginea (sometimes also referred to not quite appropriately as submucosa)
Sample 4[edit | edit source]
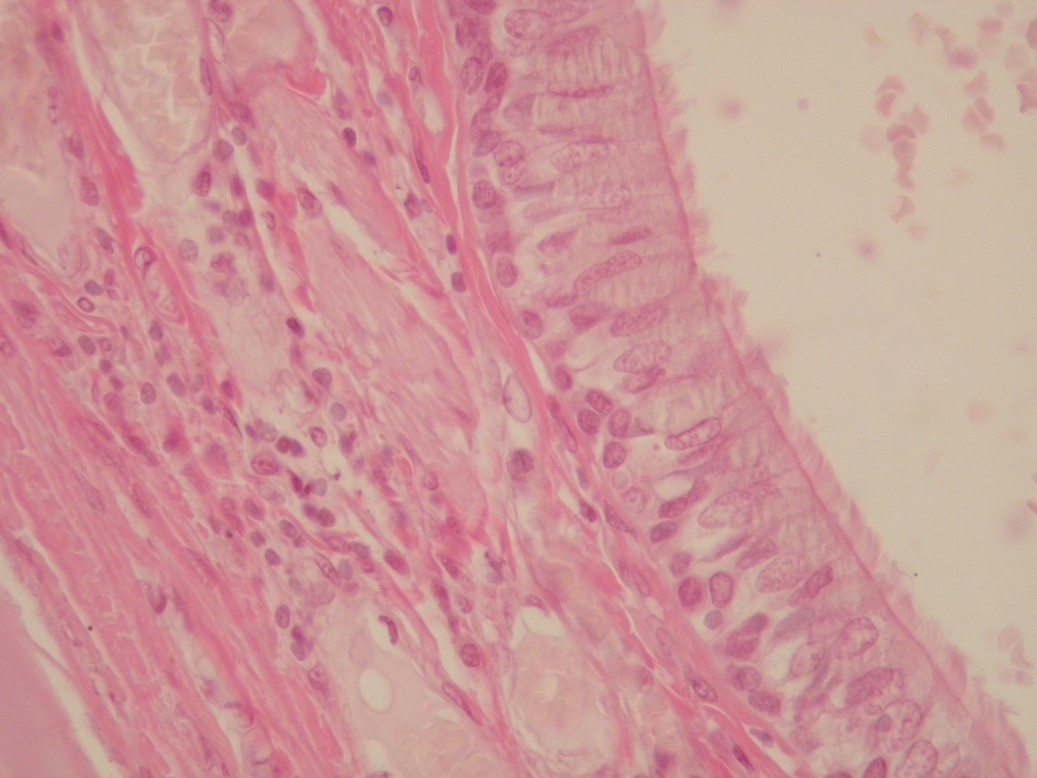
Name: Bronchus - multi-row cylindrical epithelium with cilia; HE
Description: Multiple columnar epithelium with cilia: The stronger staining line represents the basal bodies of the cilia. Nuclei are stored in multiple rows, all cells are attached to the basal lamina.
Sample 5[edit | edit source]

Title: Bronchus; HE
Description: The wall of the bronchus consists of mucosa' (multiple columnar epithelium with cilia and lamina propria mucosae - sparse collagenous tissue), tunica fibro-musculo-cartilaginea', which it contains collagen fibers with an admixture of elastic fibers, smooth muscle and hyaline cartilage. Externally, the tunica adventicia is found. In the wall of the bronchus, there are mixed seromucinous glands in the ligament. The specimen shows relatively wide ducts of these glands.
Sample 6[edit | edit source]
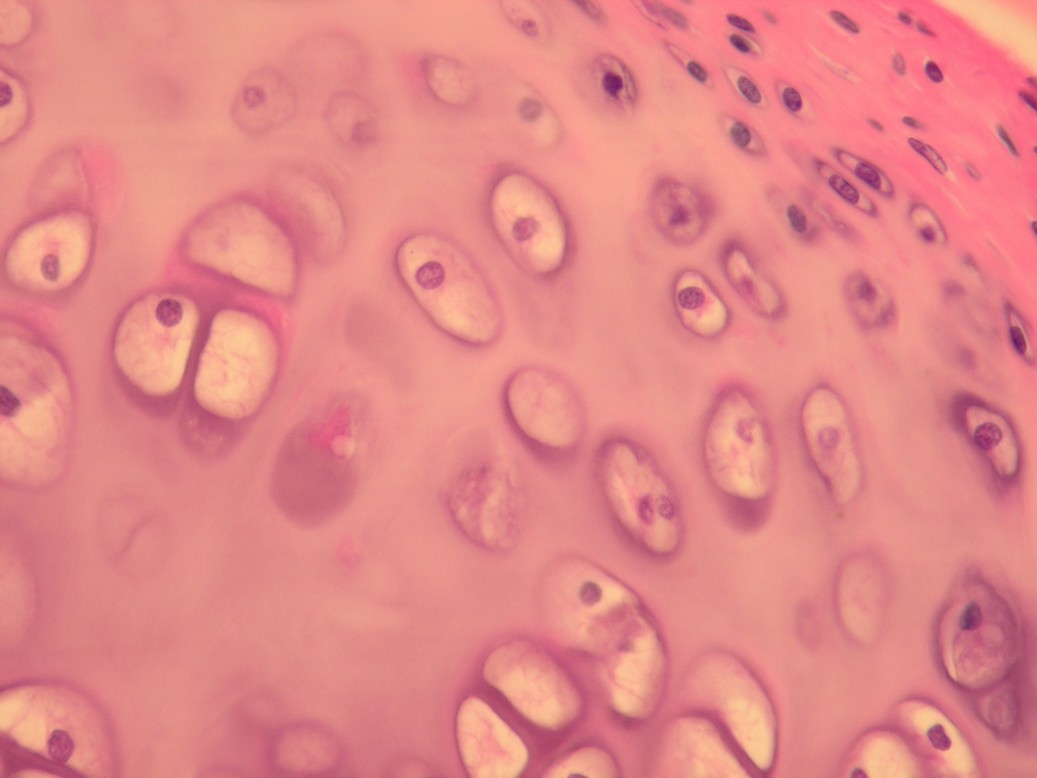
Name: Bronchus - hyaline cartilage
Description: Chondrocytes are stored in lacunae, which are surrounded by intercellular matrix. On the surface of the cartilage we see the perichondrium (collagenous ligament). The cells of the perichondrium differentiate into chondrocytes and gradually become rounded.
Sample 7[edit | edit source]
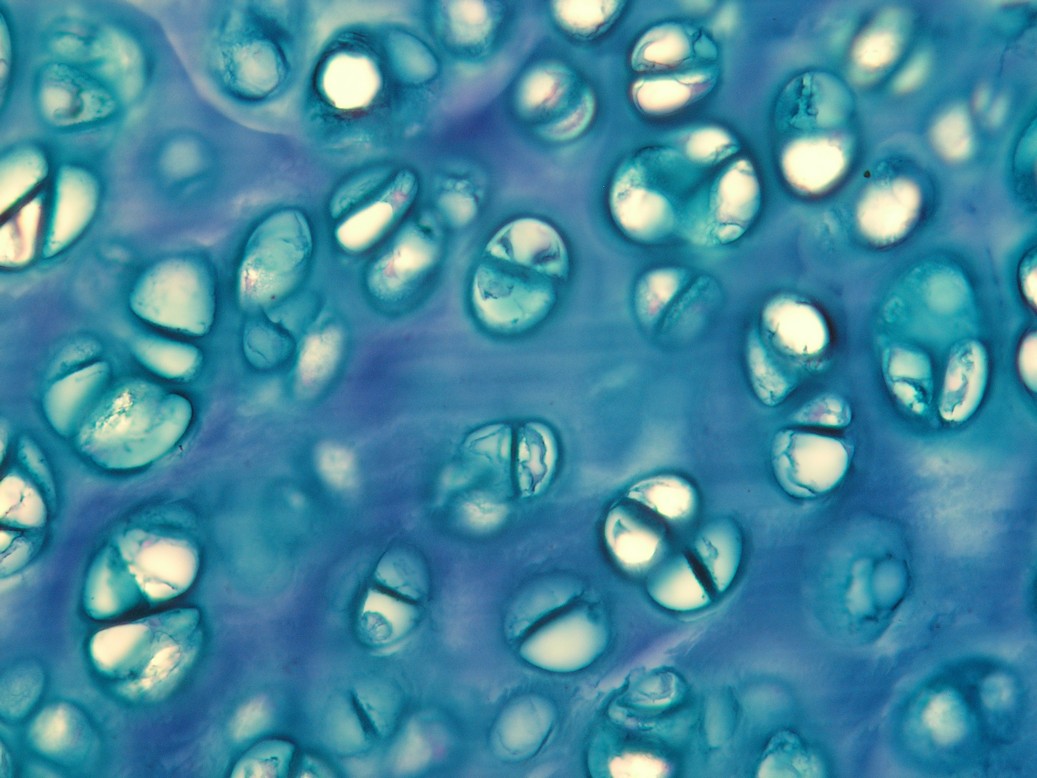
Name: Hyaline cartilage - bronchus; coloring – alcian blue
'Description: Chondrocytes lie in lacunae. Several chondrocytes lying in close proximity form an isogenetic group.
Epithelia[edit | edit source]
Mamma nonlactans (preparation)
