Bilirubin
From WikiLectures
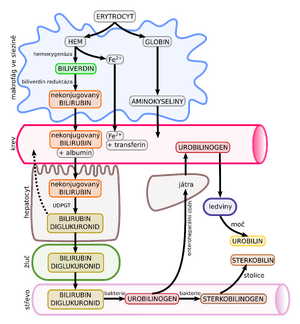
Bilirubin is a yellow substance produced by the breakdown of heme. It belongs to bile dyes. It is formed in the smooth endoplasmatic reticulum of reticuloendothelial cells (spleen, liver, bone marrow) by the action of heme oxygenase enzyme complex.
Most is excreted in the intestine as part of bile. Unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin is insoluble in water, it binds to albumin (transport from the spleen to the liver). Conjugated (direct) bilirubin (most often bilirubindiglucosiduronate) is water-soluble, it is conjugated with glucuronic acid in the liver. Reference values are 3–17 μmol/l (total bilirubin)
Related articles[edit | edit source]
References:[edit | edit source]
- MURRAY, Robert K.. Harperova biochemie. 2. edition. H&H, 1998. pp. 872. ISBN 80-7319-013-3.