The C13 urea breath test
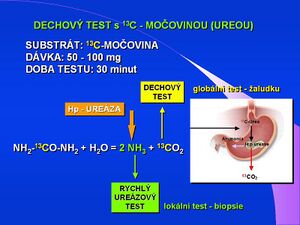
The C13 urea breath test (13C-UBT) is now considered the standard for detection of infection caused by Helicobacter pylori . The principle of the test is based on the detection of labeled carbon dioxide, which is formed by the cleavage of the substrate - urea by an enzyme, urease, which is produced as a surface protein by the bacterium Helicobacter pylori . The test method was described as early as 1987 and there are a number of modifications that differ mainly in the amount of substrate administered (50-100 mg), the administration of citric acid solution or natural orange juice and the time interval for exhaled air sampling. One of the variants is the so-called European Standard Protocol, see below.
Test Procedure[edit | edit source]
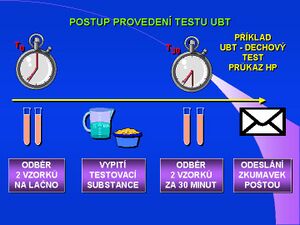
The patient must be fasted for the test (must not eat, drink or smoke for at least 2 hours). Two or three exhaled air samples are taken into a test tube. It is important to ensure that air is trapped from the final exhalation phase. This is followed by drinking 200 ml of citric acid solution or natural unsweetened orange juice and after 5 to 10 minutes 100 mg of carbon-labeled urea 13C (half 50 mg is given to children). After exactly 30 minutes, two or three exhaled air samples are taken into the tubes in the same way as at the beginning of the test. Air samples in test tubes are analyzed by IRMS technique. The protocol variant for IR - POCT analyzers differs only in that the exhaled air samples are taken in aluminum foil bags and are analyzed immediately in the outpatient clinic or laboratory, the test result is known within 10 minutes.
For the evaluation of the test, the criterion of changing the ratio of 13CO2 : 12CO2 is determined to be greater than 5 per mille between the sample at time T30 compared to the sample T0. The test result is affected by gastric motility and anatomy , impaired emptying, treatment with proton pump inhibitors , antibiotics or bismuth preparations. It is therefore recommended to perform a breath test 4-6 weeks after the end of eradication therapy. Recent studies have shown reliable evaluation of the test in children at a dose of 1 mg / kg body weight, max. 25 mg of labeled urea.
Links[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- with the permission of the author taken from KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedie laboratorních metod v gastroenterologii [online]. ©2002. The last revision 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
- SAVARINO, V – VIGNERI, S – CELLE, G. BMJ Journals : The 13C urea breath test in the diagnosis ofHelicobacter pylori infection [online]. ©1999. [cit. 2022-03-26]. <https://gut.bmj.com/content/45/suppl_1/I18>.
H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori ) Breath Test: What is It, How is it Done. Cleveland Clinic: Every Life Deserves World Class Care [online]. Copyright © 2022 Cleveland Clinic. All Rights Reserved. [cit. 28.03.2022]. Dostupné z: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diagnostics/5217-h-pylori-helicobacter-pylori-breath-test--urea-breath-test
Literature[edit | edit source]
- PENG, NJ. Comparison of noninvasive diagnostic tests for Helicobacter pylori infection. Med Princ Pract. 2009, vol. 18, no. 1, p. 57-61, ISSN 1011-7571 (Print), 1423-0151 (Electronic). PMID: 19060493.
- YANG, YJ. More economic 25 mg 13C-urea breath test can be effective in detecting primary Helicobacter pylori infection in children. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 335-9, ISSN 0815-9319 (Print), 1440-1746 (Electronic). PMID: 17295763.
- BURES, J. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection in the Czech Republic. Helicobacter. 2006, vol. 11, no. 1, p. 56-65, ISSN 1083-4389 (Print), 1523-5378 (Electronic). PMID: 16423091.
- KOPÁCOVÁ, M. Comparison of different protocols for 13C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in healthy volunteers. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2005, vol. 65, no. 6, p. 491-8, ISSN 0036-5513 (Print), 1502-7686 (Electronic). PMID: 16179282.
- OPEKUN, AR. Improved infrared spectrophotometer for point-of-care patient 13C-urea breath testing in the primary care setting. Clin Biochem. 2005, vol. 38, no. 8, p. 731-4, ISSN 0009-9120 (Print), 1873-2933 (Electronic). PMID: 15963485.
- FRUEHAUF, H. Gastroscopic real-time 13C-urea breath test. Endoscopy. 2005, vol. 37, no. 6, p. 527-31, ISSN 0013-726X (Print), 1438-8812 (Electronic). PMID: 15933924.
- HINO, B. Comparison of invasive and non-invasive tests diagnosis and monitoring of Helicobacter pylori infection in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004, vol. 39, no. 5, p. 519-23, ISSN 0277-2116 (Print), 1536-4801 (Electronic). PMID: 15572892.
- ZAMBON, CF. Non-invasive diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: simplified 13C-urea breath test, stool antigen testing, or DNA PCR in human feces in a clinical laboratory setting?. Clin Biochem. 2004, vol. 37, no. 4, p. 261-7, ISSN 0009-9120 (Print), 1873-2933 (Electronic). PMID: 15003727.
- ISRAELI, E. A novel 13C-urea breath test device for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection: continuous online measurements allow for faster test results with high accuracy. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003, vol. 37, no. 2, p. 139-41, ISSN 0192-0790 (Print), 1539-2031 (Electronic). PMID: 12869884.
- KAWAKAMI, E. 13 C-urea breath test with infrared spectroscopy for diagnosing helicobacter pylori infection in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2002, vol. 35, no. 1, p. 39-43, ISSN 0277-2116 (Print), 1536-4801 (Electronic). PMID: 12142808.
- YOSHIMURA, N. A 13C-urea breath test in children with helicobacter pylori infection: assessment of eradication therapy and follow-up after treatment. J Gastroenterol. 2001, vol. 36, no. 9, p. 606-11, ISSN 0944-1174 (Print), 1435-5922 (Electronic). PMID: 11578064.
- GRAHAM, DY. Simplified 13C-urea breath test for detection of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001, vol. 96, no. 6, p. 1741-5, ISSN 0002-9270 (Print), 1572-0241 (Electronic). PMID: 11419823.
- WANG, WM. Simplified 13C-urea breath test for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection--the availability of without fasting and without test meal. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2000, vol. 16, no. 12, p. 607-13, ISSN 1607-551X (Print). PMID: 11392100.
- BURES, J. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori with the 13C-labeled urea breath test: study methodology. Cas Lek Cesk. 2000, vol. 139, no. 24, p. 776-8, ISSN 0008-7335 (Print). PMID: 11262917.