Sentinel node
The sentinel lymph node (SLU) is the first lymph node to which tumor cells from the primary tumor are likely to spread, as it is the regional lymph node closest to the tumor. Only then does it spread to other lymph nodes.
Sentinel node examination[edit | edit source]
Thanks to the assumption that sentinel nodes are the target organs to which tumor cells from a malignant tumor primarily metastasize, a perioperative examination is performed. The SLU examination specifies the staging of the disease, the prognosis and determines the further course of systemic treatment. If the sentinel node is affected by a malignant tumor, it is necessary to examine other lymph nodes.
The SLU examination is especially important for breast cancer, melanoma, in the urological field and others.
Evidence of metastatic involvement of the nodes is possible only by histopathological analysis .
In the case when a metastatic process is not proven in the SLU, it is possible to rule out a radical dissection of the nodes .
Conducting an examination [edit | edit source]
SLU imaging is based on the representation of nodular tissue using an applied substance.
Currently, the display can be done in two ways . The first method is performed directly in the operating room, the second method is performed preoperatively in the nuclear medicine department.
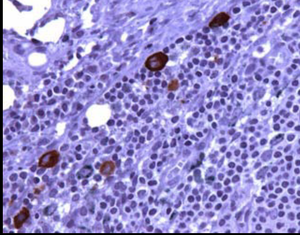
The optimal way is a combined technique using both lymphoscintigraphy and intraoperative detection using a gamma probe and staining. Sentinel lymph node positive for melanoma micrometastases
Intraoperative examination[edit | edit source]
It is performed directly in the operating room , when patent blue is applied before the procedure , which quickly reaches the lymphatic vessel and colors the first node.
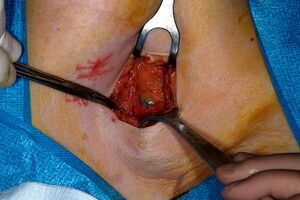
This image contains annotations.
Hover over the image to view. Sentinel's node stained patent blue, (axilla)
Lymphocitigraphy[edit | edit source]
We perform this method preoperatively at the Department of Nuclear Medicine .
A small amount of the radiopharmaceutical 99mTC Nanocolloid is applied , which penetrates the adjacent lymphatic capillaries and is transported to the first lymph node together with the lymph. Approximately 30 minutes after the application, a scintigraphy of the fallout area is performed using a hybrid SPECT/CT camera , the fallout sentinel node is marked , and the patient leaves for surgery .
This is followed by pre-operative detection of gamma radiation from the applied radiopharmaceutical with a scintillation probe directly in the operating room. It is a special hand-held probe equipped with a small detector. With its help, the surgeon before the operation specifically searches for the deposit that contains the applied radiopharmaceutical. It orients itself according to the marks drawn on the skin, according to the sound signal of the probe or according to the increased frequency of pulses. He makes an incision at the place with the most radioactivity and removes the SLU. This procedure is referred to as radiation-guided surgery. Currently, SLU lymphoscintigraphy is a staging method for breast cancer and malignant melanoma.
The lymphoscintigraphy examination of the sentinel node itself does not directly detect the metastatic process, but only determines (detects) the node that could be affected by this process with a high probability.
Contraindications are conditions after previous operations in the draining lymphatic basins or after irradiation of these areas.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ National Health Information Portal. Glossary: Sentinel lymph node [online]. Last revision 2023, [cit. 2023-03-25]. < https://www.nzip.cz/rejstrikovy-pojem/2985 >.
- ↑ MOJŽIŠOVÁ, Jaromíra and Zdeněk KOZEL. Lymphoscintigraphy to detect sentinel nodes. Florence [online] . 2017, year 2017, vol. 4, pp. 9-11, also available from < https://www.florence.cz/casopis/archiv-florence/2017/4/lymfoscintigrafie-k-detekci-sentinelovych-uzlin/ >. ISSN 2570-4915.