RDG examination for inflammation of the lower respiratory tract
Anatomy[edit | edit source]
The lower respiratory tract includes:
- larynx ,
- trachea ,
- bronchy ,
- lungs .
Epiglottitis[edit | edit source]
A typical clinic + edematous epiglottis ("thumbprint sign") is displayed on a targeted lateral X-ray.
| X-ray of the spine in lateral projection: normal image of the epiglottis, which is slender, aryepiglottic algae are unmagnified |
Croup[edit | edit source]
Typical clinic in a typical patient + subglottic narrowing ("steeple sign") on a targeted X-ray image in anteroposterior projection.
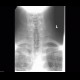
|
X-ray of the AP spine: normal image of the larynx and beginning of the trachea |
Bronchitis[edit | edit source]
In most cases, X-rays are not well known: rough bronchovascular drawing can also be caused by chronic changes.
Bronchiolitis[edit | edit source]
At HRCT a typical tree-in-bud - an image of a sprouting tree. Bronchiolitis is not the only one that can create this image.
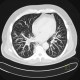
|
HRCT of the lungs: tree-in-bud in terminal bronchiolitis |

|
HRCT of the lungs: tree-in-bud in infectious bronchiolitis |
Peribronchitis[edit | edit source]
Amplification of peribronchia with small peribronchial infiltrates.
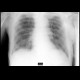
|
Chest X-ray: rough bronchovascular drawing bilaterally paracardially - reinforced bronchial wall, indicated peribronchial infiltrates |
Pneumonia[edit | edit source]
Inflammatory conditioning of the lung parenchyma with airy bronchograms and preserved volume of the lung parenchyma (x airiness or compression).
According to the range , it can be specified as:
- Allar pneumonia: pulmonary wing.
- Lobar pneumonia: pulmonary lobe.
- Segmental pneumonia: pulmonary segment.
| Chest X-ray: lobar pnemonia |
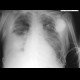
|
Chest X-ray: lobar pnemonia |
Bronchopneumonia[edit | edit source]
Combination of peribronchial changes and inflammatory condensation of the lung parenchyma.
| Chest X-ray: bronchopneumonia |
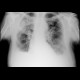
Pleurobronchopneumonia[edit | edit source]
Combination of peribronchial changes and inflammatory condensation of the lung parenchyma.
|
Chest X-ray: pleurobronchopneumonia |
Atypical pneumonia[edit | edit source]
Interstitial thickening, ground-glass in combination with infiltrates - an image that does not fall into the above categories, most often in immunocompromised patients .
| HRCT of the lungs: pneumocystis pneumonia |
| Pulmonary CT: atypical pneumonia |
Specific and granulomatous inflammations of the lung parenchyma[edit | edit source]
lung infections _ edit source ][edit | edit source]
- Aspergillus: only the colonization of the pre-formed cavity.
- Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis: cotton wool, limited deposit, thick hem.
- Aspergil bronchopulmonary aspergillosis:
- dilatation of central bronchi,
- high density mucus plugs are typical,
- bronchial wall reinforcement.
- Bronchoinvasive aspergillosis: spreads through the bronchi, grows into the wall, tree-in-bud, thickens the bronchial wall, ground-glass, mucus plugs, the image of bronchopneumonia.
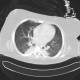
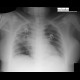
- Angioinvasive aspergillosis: a node in the lung parenchyma with a halo (typical), later cavitating, connecting to a blood vessel.
|
Pulmonary CT: angioinvasive aspergillosis |
|
Chest X-ray: angioinvasive aspergillosis |
Pulmonary tuberculosis[edit | edit source]
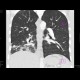
There is often a non-specific finding in active tuberculosis - a picture of multiple condensations in the peribronchial distribution, cavities, tree-in-bud, milliary spread, enlarged lymph nodes in the hilum and mediastinum.
|
HRCT of the lungs: tuberculosis |
| HRCT of the lungs: tuberculosis |
Postspecific changes in elderly patients are common:
- Peak pachypleuritis.
- Postspecific node - typically calcification.
- Fibrous stripes, hilarization.
- Calcification in nodes.
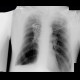
|
class="wikitable" | Chest X-ray and HRCT of the lungs: postspecific changes in the lung parenchyma |
|}
Pneumonitis[edit | edit source]
Pneumonitis is a broad heterogeneous group of non-infectious inflammations of the lung parenchyma.
Important[edit | edit source]
- In diff. Consideration is a very important clinical condition of a patient well filled out request.
- A tumor can also be hidden behind pneumonia.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
- Diagnostic imaging methods in chest examination
- Pneumonia
- Infant pneumonia • Pneumonia in older children
- Bacterial pneumonia • Atypical pneumonia
- Absent pneumonia
External links[edit | edit source]
- pictures at atlas.mudr.org
Kategorie:Radiodiagnostika
Kategorie:Vnitřní lékařství
Kategorie:Pneumologie
