Plexus choroideus (SFLT)
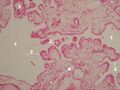
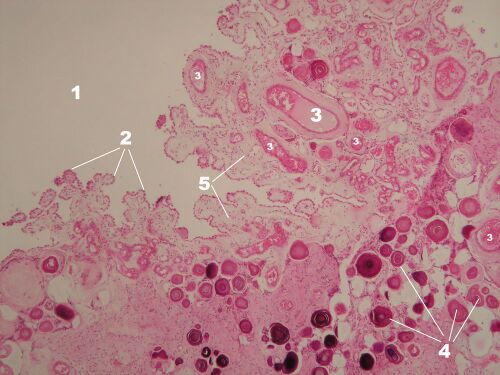
Plexus chorioideus – overview (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – lumen of the chamber, 2 – surface single-layer epithelium of the tela choroidea, 3 – vessels of the choroid plexus, 4 – acervulus cerebri (see preparation no. 5), 5 – fibrous stroma derived from the pia mater.
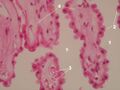
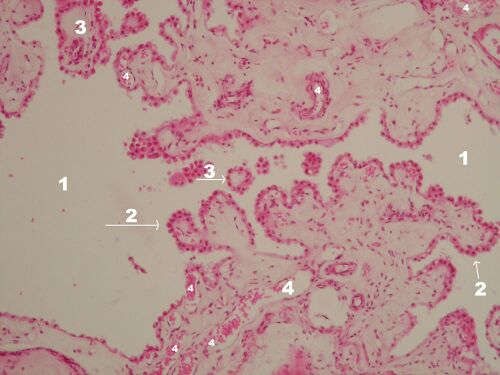
Plexus chorioideus – detail of the bush (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 –lumen of the chamber, 2 – surface single-layer epithelium of the choroid body, 3 – villi of the choroid body on a cross section, 4 – vessels of the choroid plexus.
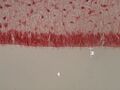
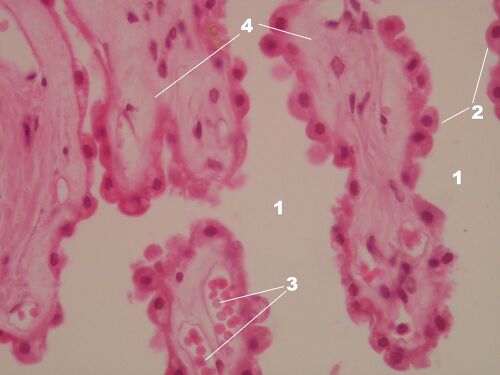
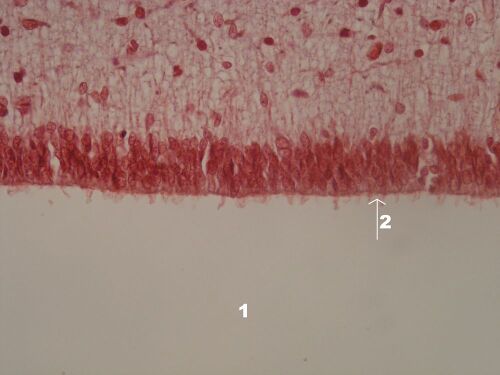
Plexus chorioideus – detail of villi (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 – lumen of the chamber, 2 – superficial single-layer epithelium of the tela choroid, 3 – vessels of the choroid plexus, 4 – fibrous stroma.
Tancyty[edit | edit source]
Description: 1 –chamber lumen, 2 – chamber surface of tanycytes with microvilli
note: tanycytes (from the Greek tanus – elongated) are morphologically specialized cells of the ependyma located at the base of III. cerebral ventricles, they differ from other ependymal cells by their long projections that extend into the hypothalamus.
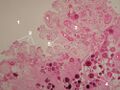
Acervulus cerebri – detail (HE)[edit | edit source]
Description: Acervulus cerebri, or brain sand, are pathological calcifications present in CNS tissue, typically in the choroid plexus and pineal gland.