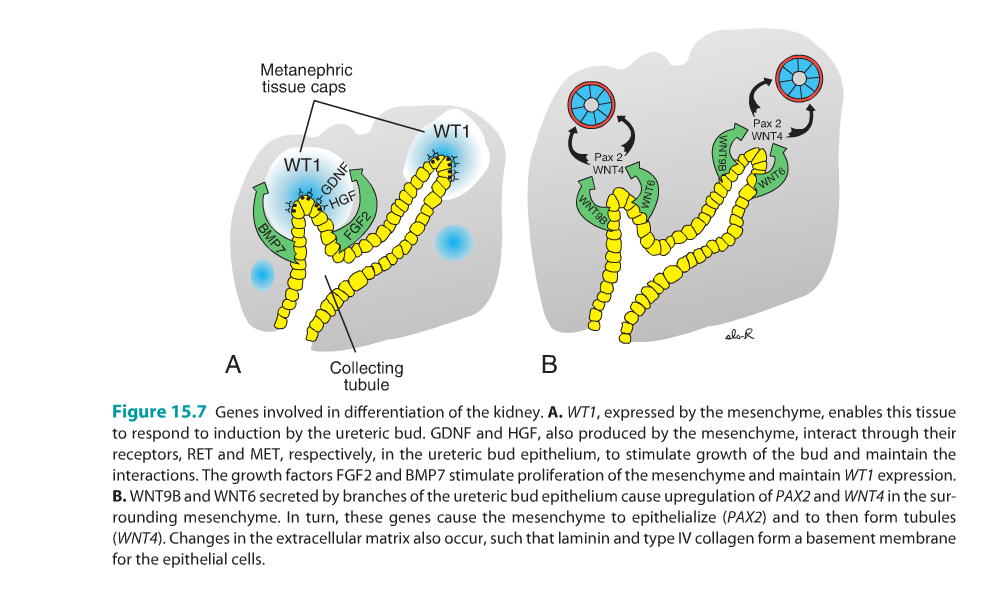
Molecular regulation of kidney
- Involves epithelial mesenchymal interactions.
- Epithelium of utereric bud from the mesonephros interacts with mesenchyme of the metanephric blastema
Mesenchyme expresses WT1- transcription factor that makes this tissue competent to respond to induction by the ureteric bud.
WT1 also regulates production of GLIAL-DERIVED NEUROTROPHIC FACTOR (GDNF) and HEPATOCYTE GROWTH FACTOR (HGF/SCATTER FACTOR) by the mesenchyme, these proteins stimulate branching and growth fo the ureteric buds.
The TYROSINE KINASE RECEPTOR RET for GDNF and MET for HGF are synthesized by the epithelium of the ureteric buds. This establishes a signalling pathways between the 2 tissues
Buds induce the mesenchyme via FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTOR 2 (FGF2) and BONE MORPHOGENIC PROTEIN 7 (BMP7)
Both of these growth factors block apoptosis and stimulate proliferation in the metanephric mesenchyme while maintaining production of WT1.
Conversion of mesenchyme to epithelium for nephron formation is also mediated by ureteric buds thorough expression of WNT9B and WNT6 which upregulate PAX2 and WNT4 in the metanephric mesenchyme.
PAX2 promotes condensation of mesenchyme to epithelialize and form tubules. Because of these interactions, modifications in the extracellular matrix also occur.
Fibronectin, collagenI collagen III are replaced by laminin and type IV collagen, which is a characteristic of an epithelial basal lamina.
The cell adhesion molecules SYNDECAN and E CADHERIN, which are essential for condensation of the mesenchyme into an epithelium, are synthesized.
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
SADLER, Thomas, et al. Langman's Medical Embryology. 10. edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006. 371 pp. ISBN 978-0781794855.