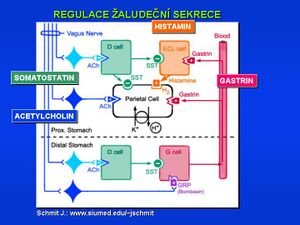
Gastrin in serum
Gastrin is a hormone of polypeptide character (the molecule consists of 17 amino acids, Mr = 2,100), which occurs in three forms: the basic molecule is G-17 (little gastrin), the others are G-34 (big gastrin) and G-13 ( mini gastrin with a shortened chain to 13 amino acids). A pentapeptide with a C-terminal gastrin sequence (β-Ala-Trp-Met-Asp-Phe-NH2), called pentagastrin, is used to stimulate gastric acidity.
Gastrin level[edit | edit source]
Serum gastrin levels are usually determined by the RIA method, there are also ELISA variants of immunochemical evidence. Normal values of 25–100 ng / l are significantly increased especially in Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (gastrinoma, pancreatic tumor with overproduction of gastrin), when we show a 10–1000-fold increase in gastrin levels, which, however, fluctuates significantly during the day; 20-40% can capture normal gastrin levels. Due to the existence of three forms of gastrin, the result of the assay depends on the type of antibody used in the test. Methods for the determination of gastrin are standardized for synthetic gastrin G-17, the determination of forms G-34 and G-13 depends on the cross-reactivity with the respective antibody. The normal ratio of forms G-13: G-17: G-34 is 8: 2: 1, on an empty stomach there is a higher proportion of forms G-34, after eating forms G-17 and G-13.
Determination of gastrin[edit | edit source]
The determination of gastrin is part of the gastrin stimulation test, where we determine a 90-minute profile (in 9 serum samples) after stimulation with insulin, secretin or Ca-gluconate. The determination of gastrin-17, pepsinogen I and antibodies to Helicobacter pylori class IgG is offered by the so-called GastroPanel, which is a non-invasive, laboratory parameter to assess Helicobacter pylori infection, atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer risk. The issue of determination of gastrin on an empty stomach and after stimulation and the diagnostic significance in the pathology of gastroduodenal diseases, including gastric cancer, are also discussed.
Links[edit | edit source]
Source[edit | edit source]
- With permission of the author taken from: KOCNA, Petr. GastroLab : MiniEncyklopedia of laboratory methods in gastroenterology [online]. ©2002. Last revision 2011-01-08, [cit. 2011-03-04]. <http://www1.lf1.cuni.cz/~kocna/glab/glency1.htm>.
References[edit | edit source]
- CAO, Q, et al. Screening of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer by serum pepsinogen, gastrin-17 and Helicobacter pylori immunoglobulin G antibodies. J Dig Dis. 2007, vol. 8, no. 1, s. 15-22, ISSN 1751-2972 (Print), 1751-2980 (Electronic). PMID: 17261130.
- LOPES, AI, et al. Relationship among serum pepsinogens, serum gastrin, gastric mucosal histology and H. pylori virulence factors in a paediatric population. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006, vol. 41, no. 5, s. 524-31, ISSN 0036-5521 (Print), 1502-7708 (Electronic). PMID: 16638693.
- GERMANÁ, B, et al. Clinical usefulness of serum pepsinogens I and II, gastrin-17 and anti-Helicobacterpylori antibodies in the management of dyspeptic patients in primary care. Dig Liver Dis. 2005, vol. 37, no. 7, s. 501-8, ISSN 1590-8658 (Print), 1878-3562 (Electronic). PMID: 15975537.
- OHKUSA, T, et al. Improvement in serum pepsinogens and gastrin in long-term monitoring after eradication of Helicobacter pylori: comparison with H. pylori-negative patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004, vol. 20, Suppl 1, s. 25-32, ISSN 0269-2813 (Print), 1365-2036 (Electronic). PMID: 15298602.
- KONTUREK, SJ, et al. Serum progastrin and its products, gastric acid secretion and serum pepsinogen I in gastric cancer. Digestion. 2003, vol. 68, no. 4, s. 169-77, ISSN 0012-2823 (Print), 1421-9867 (Electronic). PMID: 14671424.
- VÄÄNÄNEN, H, et al. Non-endoscopic diagnosis of atrophic gastritis with a blood test. Correlation between gastric histology and serum levels of gastrin-17 and pepsinogen I: a multicentre study. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003, vol. 15, no. 8, s. 885-91, ISSN 0954-691X (Print), 1473-5687 (Electronic). PMID: 12867799.
- BROUTET, N, et al. Pepsinogen A, pepsinogen C, and gastrin as markers of atrophic chronic gastritis in European dyspeptics. Br J Cancer. 2003, vol. 88, no. 8, s. 1239-47, ISSN 0007-0920 (Print), 1532-1827 (Electronic). PMID: 12698190.
- KONTUREK, JS, et al. Helicobacter pylori and CagA status, serum gastrin, interleukin-8 and gastric acid secretion in gastric cancer.. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002, vol. 37, no. 8, s. 891-8, ISSN 0036-5521 (Print), 1502-7708 (Electronic). PMID: 12229962.
- SIPPONEN, P, et al. Serum levels of amidated gastrin-17 and pepsinogen I in atrophic gastritis: an observational case-control study.. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2002, vol. 37, no. 7, s. 785-91, ISSN 0036-5521 (Print), 1502-7708 (Electronic). PMID: 12190091.
- LANGER, P, et al. Prospective controlled trial of a standardized meal stimulation test in the detection of pancreaticoduodenal endocrine tumours in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Br J Surg. 2001, vol. 88, no. 10, s. 1403-7, ISSN 0007-1323 (Print), 1365-2168 (Electronic). PMID: 11578300.
- BERMEJO, F, et al. Basal concentrations of gastrin and pepsinogen I and II in gastric ulcer: influence of Helicobacter pylori infection and usefulness in the control of the eradication.. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001, vol. 24, no. 2, s. 56-62, ISSN 0210-5705. PMID: 11247290.
- BERGER, AC, et al. Prognostic value of initial fasting serum gastrin levels in patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. J Clin Oncol. 2001, vol. 19, no. 12, s. 3051-7, ISSN 0732-183X (Print), 1527-7755 (Electronic). PMID: 11408501.
- GOEBEL, SU, et al. Prospective study of the value of serum chromogranin A or serum gastrin levels in the assessment of the presence, extent, or growth of gastrinomas. Cancer. 1999, vol. 85, no. 7, s. 1470-83, ISSN 0008-543X (Print), 1097-0142 (Electronic). PMID: 10193936.
- OBERG, K, et al. The ultimate biochemical diagnosis of endocrine pancreatic tumours in MEN-1. J Intern Med. 1998, vol. 243, no. 6, s. 471-6, ISSN 0954-6820 (Print), 1365-2796 (Electronic). PMID: 9681845.