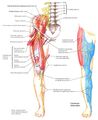
Femoral nerve
The femoral nerve is the major peripheral nerve of the lower limb. Originating from the anterior rami of nerve roots L2-L4.
Anatomical course[edit | edit source]
Arises from L2-L4 of the lumbar plexus. The nerve travels inferiorly through the psoas major muscle. It supplies branches to the iliacus and pectineus muscles.Then passes underneath the inguinal ligament to enter the femoral triangle. Within this triangle, the nerve is located lateral to the femoral artery. Beyond the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve divides into anterior and posterior divisions.
- Anterior divisions are anterior cutaneous branches, Branch to sartorius, Branch to pectineus
- Posterior divisions are Saphenous nerve( the terminal cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve), Branches to quadriceps femoris
Functions[edit | edit source]
Motor functions: Innervates the anterior thigh muscles - pectineus, iliacus, sartorius that flexes the hip and quadriceps femoris: rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis and vastus intermedius which extends the knee.
Sensory functions: anterior cutaneous branches of the femoral nerve supplies cutaneous branches to the anteromedial thigh. Saphenous nerve supplies the medial side of the leg and foot .
Clinical Significance[edit | edit source]
Femoral neuropathy[edit | edit source]
Occurs when there is damage or dysfunction to the femoral nerve. Causes of femoral nerve palsy:
- Trauma: Direct trauma to the femoral nerve, such as from a sports injury, car accident, or surgical procedure in the pelvic area, can cause damage.
- Compression: Compression of the femoral nerve can occur due to conditions like pelvic tumors, hernias, or prolonged pressure on the nerve during activities like prolonged squatting or sitting cross-legged.
- Diabetes: Long-standing uncontrolled diabetes can lead to nerve damage (diabetic neuropathy)
- Inflammation: Conditions such as infections or autoimmune diseases can cause inflammation of the femoral nerve.
Symptoms of femoral nerve palsy can vary depending on the severity and cause[edit | edit source]
- Weakness: Difficulty in extending the knee or lifting the leg.
- Numbness or tingling: Sensory disturbances in the front of the thigh or inner lower leg.
- Pain: Sharp or shooting pain in the thigh, groin, or inner lower leg.
- Difficulty walking: Due to weakness or pain
Femoral nerve causes patellar tendon reflex, stripping of varicosed saphenous vein and femoral nerve block are other areas of clinical relevance for femoral nerve.[edit | edit source]
Links[edit | edit source]
https://teachmeanatomy.info/lower-limb/nerves/femoral-nerve/ Accessed on 07/05/2024.
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/femoral-nerve Accessed on 07/05/2024.
https://www.physio-pedia.com/index.php?curid=25593 Accessed on 07/05/2024.