Ergometry (2. LF UK)
Job Entry[edit | edit source]
- Verification of the physical relation .
- Examination with graded load without breaks.
- Examination with graded load with breaks.
- Comparison of the fitness of two people using the Kettler World Tours program (alternatively).
Theoretical introduction[edit | edit source]
Ergometry is an examination that monitors the activity of the heart during exercise, thanks to which it is possible to diagnose some types of heart disorders that cannot be detected when a person is at rest. Before starting the actual examination, a control ECG curve is recorded for the patient lying at rest. In the presence of the doctor, the patient is exposed to an increasing load on the so-called ergometer (exercise bike, treadmill...) and is also connected to an EKG that monitors heart activity during the entire examination. After the test, the result is interpreted by an experienced cardiologist.
Note: For practice purposes, we do not use ECGs, but only pulse rate meters.
As the physical load increases, the muscles demand more oxygen and energy, as a result, the arteries in the stressed area expand and the heart activity also increases. However, if the vessels are blocked by fatty plaques (atherosclerosis), this dilation and insufficient oxygenation of the area of the heart supplied by the narrowed vessel does not occur, causing severe chest pain.
A doctor may recommend an examination in several of the following cases:
- detection of heart diseases and their nature
- as a control of the course of heart disease
- after acute myocardial infarction and cardiac catheterizations (coronary artery surgery)
- to determine the effectiveness of drugs, or change medication
- determination of tolerable load during sports and other physical activity
- assessment of other heart defects and arrhythmias
The examination usually consists of several parts:
- Preparatory phase: connecting the person to the devices, measuring the resting pulse rate
- 'Warm up phase (warm up): application of low load with the aim of increasing tissue blood flow, oxygen supply and metabolism, improving joint mobility, the phase also has a preventive effect against ischemia of the heart and arrhythmias
- Load phase: load progression varies according to the type of machine and the performance of the examined patient
- 'Cool down phase (cool down): low-intensity exercise with the aim of returning circulatory parameters after intense exercise to values close to rest and preventing dizziness or collapse, facilitating the removal of lactate from the blood
- Recovery phase: monitoring the relaxation after exercise
Precautions before starting the test.[edit | edit source]
Persons who are in any way medically indisposed (severe heart rhythm disorders, injuries, inflammatory diseases, lung problems,...) may not participate in the test. Eat sensibly and dress athletically before the test. Don't forget to drink enough fluids. Enter the ergometer without shoes. During the test, the rest of the group does not move around the ergometer to avoid injury. Ventilate the room as needed. Complications such as acute myocardial infarction (0.05%), sudden death (0.01%), or less serious disorders (mechanical injuries, dizziness, weakness...) may occur during the examination. If you feel any health problems during the test, stop the test immediately.
Home Preparation[edit | edit source]
Procedure[edit | edit source]
Tools:[edit | edit source]
- Elliptical ergometer Kettler SKYLON S (calculates work from the force needed to overcome the resistance of the machine)
- Chest belt ‒ pulse rate meter
- Sportswear
1. Task ― Verification of the physical relationship .[edit | edit source]
- Pedal fast or slow to find out when you need to exert more or less force to maintain constant power (same revolutions).
- In the protocol, describe what you observed and explain.
2. Task ― Examination with a graded load without breaks.[edit | edit source]
- Indicate the name of the team member who will be investigated in the protocol. In the appropriate fields, fill in gender, weight, age, resting pulse rate and information on whether the person in question is an athlete, i.e. state other reasons that could affect the results of the examination (current/permanent health problems, whether the examinee is a smoker, etc.).
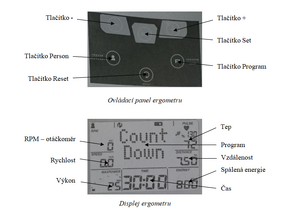
- First, reset the ergometer with the Reset button.
- After repeatedly pressing the Program button, select Count down.
- Using the Set', - and + buttons, set the time (time) to 15 min.
- Click on Set until you get to the default screen.
- Then check whether the load (power) is 25 W or adjust using - and + buttons.
- After setting up, the examinee puts a belt on his chest to measure the pulse rate.
- Measure the subject's resting pulse rate.
- The examined person warms up (warm-up + e.g. jogging in place).
- After this warm-up, the patient steps onto the ergometer. He starts running and maintains a frequency between 60-65 min-1 (RPM reading at the top left of the display) throughout the investigation. After 3 minutes, read the following values: RPM, speed, load, pulse rate, distance traveled, energy burned. Write the values in the table in the log and increase the load to 45 W. After three minutes, read these values again and increase the load to 70 W. After another three-minute block and after reading the values, increase to 95 - 120 W.
- After 15 minutes, the set program ends. Reduce the load to 30W and slowly cool down for about another two minutes (at a lower RPM). Then sit down and measure your pulse rate after three minutes.
3. Task ― Examination with a graded load with breaks.[edit | edit source]
- The subject will repeat the same procedure as in the previous task, this time with two-minute breaks between individual blocks.
- Then compare the values and justify the differences between the examinations in the discussion.
- With the protocol, don't forget to submit the graph of the dependence of the pulse on time.
4. Task ― Comparing the fitness of two people using the Kettler World Tours program (alternatively).[edit | edit source]

- List the names of the team members who will be investigated in the log. Enter gender, weight, age, resting pulse rate and information on whether the person in question is an athlete in the appropriate boxes, and indicate other reasons that could affect the test results.
- Open the Kettler World Tours program and create an account for both investigated persons (just fill in the marked fields).
- Log in to the account of the person under investigation.
- Even before starting the examination on the ergometer, measure your resting pulse rate.
- After logging in the examined person, select the training mode (IPM Run 15 min.) in the program. Even before starting it, set the maximum heart rate that the program will record (set it as high as possible, if you don't do it, there is a risk that the program will turn off before 15 min.). Do the same before starting the first and second measurements. The measured values must be the same for both measurements.
- Put on a chest strap or use a pulse rate measuring device that you attach to your ear.
- Let the examined person warm up.
- When the patient steps on the ergometer, start the IPM Run.
- The subject should try to keep the RPM around the value displayed on the monitor.
- The program will be on its own after 5 or Change the load every 10 minutes, you still need to follow the RPM value according to the monitor.
- After approximately 15 minutes, the training will end by itself and display the curve of the examined person. On it, you can observe different values depending on time (for example, pulse, power).
- Take a screenshot of this graph (Alt+Print Screen) and Ctrl+V to paste into the log.
- Measure the pulse of the examined person even 3 minutes after the end of the training. Also write the result in the log.
- The same activities will be repeated by the second person under investigation.
- Compare the graphs of both examinations: On the main page of the program where you log in, select Analyze. You check the users you want to compare. Hold Ctrl and select which records you want to compare. Click on Analyze and you will see a graph with two different colored lines. Select which values you want to compare (the pulse value is the most important). Paste a screenshot of the graph into the log.
- Compare the final values and justify the differences between the examinations.
Review Questions[edit | edit source]
Attachments[edit | edit source]
Links[edit | edit source]
- Ergometry
- https://vysetreni.vitalion.cz/ergometrie/
- http://www.kardioprachatice.cz/pages/ergometricke_vysetreni/custom_page.htm/custom_page.htm;jsessionid=13E6AF19208FFEA5E22CCD3F57060239
- http://www.stefajir.cz/?q=zatezova-ergometrie
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3761733/
Literature[edit | edit source]
- Amler E. et al. Practical tasks from biophysics I. Department of Biophysics, Charles University, 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Prague 2006
- 'Navrátil L.et al. Medical Biophysics, Grada Prague 2005