Development of Blastocyst
From WikiLectures
Cleavage
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes a series of mitotic divisions, resulting in the formation of blastomeres, which are progressively smaller with each cleavage division.
- By the eight-cell stage, blastomeres form a loosely arranged [1]clump. However, after the third cleavage, compaction occurs, leading to the formation of a compact ball of cells held together by tight junctions.
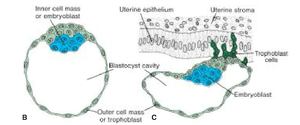
- Compaction segregates inner cells, which communicate extensively by gap junctions, from outer cells. Approximately 3 days after fertilization, the compacted embryo forms a 16-cell morula, with inner cells comprising the inner cell mass (ICM) and surrounding cells forming the outer cell mass. The ICM gives rise to tissues of the embryo proper, while the outer cell mass forms the trophoblast, contributing to the placenta.
Development of Blastocyst
- As the morula enters the uterine cavity, fluid penetrates through the zona pellucida into the intercellular spaces of the inner cell mass, eventually forming a single cavity known as the blastocele, transforming the embryo into a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst consists of an inner cell mass, now called the embryoblast, located at one pole, and an outer cell mass, or trophoblast, which flattens and forms the epithelial wall of the blastocyst.[2]
- Implantation begins as trophoblastic cells over the embryoblast pole penetrate between the epithelial cells of the uterine mucosa around the sixth day after fertilization.
- Initial attachment of the blastocyst to the uterus is mediated by L-selectin on trophoblast cells and its carbohydrate receptors on the uterine epithelium, similar to leukocyte-endothelial interactions.
- Further attachment and invasion involve integrins, laminin, and fibronectin, which regulate trophoblast differentiation, leading to mutual trophoblastic and endometrial action, facilitating implantation by the end of the first week after fertilization.[3]