Biological treatment methods in psychiatry
Biological non-pharmacological procedures are among the oldest treatment modalities of serious mental conditions. The earliest mention comes from the Indian Vedas, which describe the treatment of melancholic conditions with the help of a trained elephant, which causes the patient tied to a medical shock with convulsions.
Hippocrates described the beneficial effect of the hellebore (genus Helleborus ) on human psychopathology. The decoction is caused by generalized tonic-clonic seizures ( GTCS ).
Their development was conditioned mainly by insufficient knowledge of psychopharmacological and psychotherapeutic procedures. The use of direct current on the central nervous system, now known as transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), is not a complete novelty in the arsenal of biological methods in psychiatry. As early as 1801, the Bologna physician Giovanni Aldini, nephew of the famous Luigi Galvani (who was said to be a literary masterpiece of Frankenstein's novel in Mary Shelley), applied galvanic currents (DC) in an effort to treat melancholy in his patients.
Electroconvulsive therapy (EKT, ECT) was introduced in the late 1930s by Italian doctors who loved pork ham (Bini, Cerletti, 1938).
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) is based on the "simple physical principle" - electromagnetism , ie the duality of electric current and magnetic field postulated by Maxwell in 1855 on the basis of very complex mathematical proofs of field theory . In principle, each of us can build a simple device (with a little exaggeration) at home (as evidenced by the resources available on the Internet after entering the password "transcranial stimulation homemade youtube" into the search engine).
Trepanic and healed skulls from the Stone Age have also been found in the Czech lands. "Modern" attempts to use so-called ablative surgery to treat mental illness date back to 1891 (Burckhardt, 1891). (2) The infamous Walter J. Freeman, who performed about 3,500 lobotomies, often in completely bizarre indications.
Today's neuropsychosurgery involves a number of procedures. Deep brain stimulation is intensively developed. In other neurosurgical procedures, white matter pathways are usually selectively interrupted - but they take on a far more precise and precise form in the form of stereotactically guided microneurosurgical procedures (Lexell's gamma knife). The main area of neurosurgery is the implantation of stimulation electrodes not only into the central nervous system, but also on the peripheral cranial nerves - the left vagus nerve - in an effort to influence epileptic or affective symptoms.
Last but not least, methods that are based on common sense ("where the sun doesn't go" or "in a healthy body") come to the fore, but are supported by a number of extensive studies and meta-analyzes. It is a developing field of chronobiotherapy , consisting in the synchronization of circadian rhythms with the help of bright light (phototherapy), the use of sleep deprivation and lifestyle adjustment in an effort to treat not only (seasonal) depressive episodes but also improve cognitive performance or delirium in dementia patients.
The importance of a healthy lifestyle is repeatedly emphasized. A varied nutritionally adequate diet enriched with aerobic exercise and regular exercise.
With the development of evidence-based psychopharmacology and psychotherapy, biological methods such as obsolete or even medieval tortures gradually abandoned in the 1950s. However, in the last two decades (early 21st century) these methods have experienced a renaissance - especially in connection with the development of knowledge about neuronal and neurotransmitter systems, immune functions and (deeper knowledge of quantum theory) involved in mood regulation, thinking and behavior, studied in situ in in real time, especially with the help of rapidly evolving imaging techniques, the study of molecular and biochemical processes and, on the basis of deeper genomic and prosthetic knowledge, a closer look at everyday psychopathology.
The limits of current psychopharmacological and psychotherapeutic treatment are increasingly described, both due to the spectrum of side effects, the duration of the onset of action, but also due to the resistance to pharmacological treatment. The division of methods in this article by century is only arbitrary and rather indicates the potential for future development.
It would be appropriate to rewrite this text. Thank you-
1 *
"The purpose of all these methods is to alleviate , bridge or completely rid the patient of the dangerous symptoms of the disease, which can, in the worst case, endanger his life . We mean above all:"
Content[edit | edit source]
- 1Distribution
- 1.1Electroconvulsive therapy
- 1.2Chronobiotherapy
- 1.2.1Sleep deprivation
- 1.2.2Bright light treatment
- 1.3Psychosurgery
- 1.4Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
- 2Links
- 2.1related articles
- 2.2Source
Distribution[edit | edit source]
Biological treatment modalities in neuropsychiatry include:
I. invasive procedures
- psychosurgery;
- deep brain stimulation (DBS);
- vagus nerve stimulation (VNS);
II. minimally invasive procedures:
- electroconvulsive therapy (ECT);
- magnetoconvulsive therapy (MST);
- focal electrically administered convulsive therapy (FEAST);
III. non-invasive procedures:
- non-convulsive:
- lower intensity magnetic field:
- repetitive transcranial brain stimulation (rTMS);
- higher intensity electric field:
- transcranial DC stimulation (tDCS);
- lower intensity magnetic field:
- chronobiological.
Electroconvulsive therapy[edit | edit source]
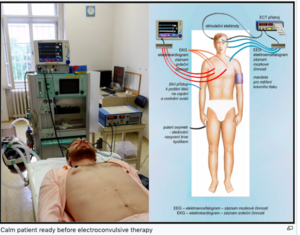
You can find more detailed information on the page Electroconvulsive therapy . Calm patient ready before electroconvulsive therapy Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a minimal invasive stimulatory biological treatment method for neuropsychiatric diseases, in which a modulated electric current is applied under general anesthesia with scalp electrode muscle relaxation in order to influence the patient's psychopathology. In some indications, it is the only - life-saving (ultimum refugium) - treatment modality.
Chronobiotherapy[edit | edit source]
Sleep deprivation[edit | edit source]
Sleep deprivation treatment uses the knowledge that some depressed patients experience a temporary improvement in mood after a sleepless night.
Can be divided into:
- complete sleep deprivation - the patient does not sleep for 40 hours;
- partial sleep deprivation - the patient is awakened after midnight.
Indications : unipolar depression - effective in 60% of patients.
Contraindications : bipolar affective disorder .
Bright light treatment[edit | edit source]
Lamp glowing bright light Some depressions have a seasonal course , especially the period March - November. These patients were often helped to travel to countries with strong sunshine for most of the day. Based on this fact, a bright light treatment was developed.
Light is used - at least 2500 lux , which is applied every morning for about 1 hour . This is how he corrects circadian rhythms.
Indication:
- seasonal depressive disorder ,
- premenstrual syndrome ,
- jet-lag syndrome - difficulties arise during a rapid transition through time zones (aircraft).
The first improvement is usually after 3-4 days of treatment.
Psychosurgery[edit | edit source]
Modern stereotactic surgery strives for the greatest possible specificity of the intervention and the least possible overall brain damage.
Used:
- electrical coagulation ,
- gamma knife ,
- microwaves ,
- radiopharmaceuticals .
It is considered the method of last choice for otherwise uncontrollable conditions.
Indications :
- The only worldwide agreement is a malignant drug-resistant form of OCD .
- In the US and GB, this therapy is also recognized in drug-resistant depression .
- In addition, it is permitted in Europe for pathological aggression .
Execution conditions :
- the patient must give consent;
- commissions must meet, etc.
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation[edit | edit source]
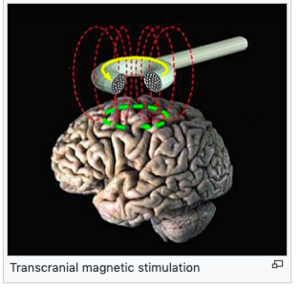
Transcranial magnetic stimulation See the Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation page for more information .
It uses the ability of the magnetic field to induce secondary electric currents of about one hundred thousandth of the primary current. Non-invasive electrical stimulation can be achieved without inducing epileptic paroxysm. It uses an induction field of 1-2.5 T (similar to MR , but in a smaller volume).
In principle, it is the use of the laws of electricity and magnetism. The strong magnetic field (around 2 T) created by the passage of current through the stimulation coil induces a synchronized depolarization of dipoles on the membranes of neurons after passing through the soft tissues of the head, skull and brain sheaths. The exact neurobiological mechanism of action on mood disorders is currently unknown.
Indications :
- depression - stimulation of the left prefrontal area,
- mania - right prefrontal area,
- anxiety disorders - OCD,
- schizophrenia .
This method is still in its infancy.
Links[edit | edit source]
https://www.wikiskripta.eu/index.php?curid=6156
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
- Electroconvulsive therapy
Source[edit | edit source]
- BENEŠ, Jiří. Study materials [online]. [feeling. 2009]. < http://jirben.wz.cz >.
- RABOCH, Jiří and Petr ZVOLSKÝ, et al. Psychiatry. 1st edition. Prague: Galén, 2001. 622 pp. ISBN 80-7262-140-8 .
- ALBRECHT, Jakub. Biological treatment of not only resistant conditions. Postgraduate Medicine [online] . 2014, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 590-594, also available from < https://zdravi.euro.cz/clanek/postgradualni-medicina/biologicka-lecba-nejen-rezistentnich-stavu-475778 >. ISSN 1212-4184.