Osteofascial spaces of the upper limb
Fascia, or muscle bundle, is a ligament surrounding a muscle. Fascia also covers entire groups of muscles and the surface of individual sections of the human body (superficial fascia).
The osteofascial (intermuscular) septum xtends from the superficial fascia to the periosteum of the bone separating the space (spatium) for a group of muscles.
The osteofascial space is closed by the skeleton, fascia and the respective osteofascial septa.
Fascia of the upper extremity[edit | edit source]
Fascia deltoidea[edit | edit source]
The superficial thoracic fascia passes into the deltoid fascia at the front, and the dorsal superficial fascia at the back. Attached to the acromion, clavicula and spina scapulae.
Fascia brachii[edit | edit source]
A continuation of the deltoid fascia on the arm. Connected to the humerus by the septum intermusculare brachii mediale et laterale, which draw the superficial fascia into the longitudinal depressions sulcus bicipitalis medialis et lateralis. Attached to both epicondyles of the humerus.
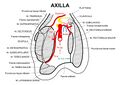
Fascia axillaris[edit | edit source]
A continuation of the fascia brachii, the fascia passes over the plica axillaris anterior et posterior. Taken together with the skin into the axila as plica axillaris.
Fascia antebrachii[edit | edit source]
It continues to the surface of the forearm from the fascia brachii, attached to the dorsal border of the ulna. Sends to the radius the anterior and posterior forearm septum. On the wrist it is reinforced dorsally in the retinaculum musculorum extensorum, ventrally in the ligamentum carpi palmare (it merges with the deeper retinaculum musculorum flexorum).
Fasciae manus[edit | edit source]
Palmarally and dorsally, they connect to the fascia antebrachii, ending at the level of the metacarpophalangeal joints.
Dorsally three layers of fascia:
- fascia dorsalis manus superficialis –attached to rad. edges of the 1st metacarpal and ulna. edges of the 5th metacarpal;
- fascia dorsalis manus intertendinea – connects the tendons on the back of the hand;
- fascia dorsalis manus interossea – connects the back. edges of metacarpals, covers mm. interossei.
Palmar two layers of fascia:
- fascia palmaris superficialis – attached to the rad. edges of the 1st metacarpal and ulna. edges of the 5th metacarpal, covers the thenar and hypothenar muscles, fused in the middle with the palmar aponeurosis;
- fascia palmaris interossea – connects the palm. metacarpal surfaces, from palms. side covers mm. interossei.
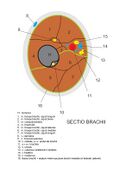
Osteofascial spaces of the arm[edit | edit source]
The longitudinally running intermuscular septa sulcus bicipitalis medialis et lateralis together with the humerus and fascia brachii close the anterior and posterior osteofascial space of the arm, containing the ventral and dorsal group of muscles of the arm. Between the ventral muscles of the arm and the lateral group of forearm muscles (beginning at the humerus), a septum, arises at the distal end of the arm , which separates the lateral muscles of the forearm.
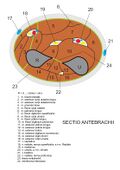
Osteofascial spaces of the forearm[edit | edit source]
The attachment of the fascia antebrachii to the dorsal edge of the ulna creates an interface between the anterior and posterior osteofascial spaces, that is, between the ventral and dorsal groups of forearm muscles. The anterior and posterior forearm septum, attached to the radius, separate the osteofascial space for the lateral group of muscles, i.e. lat. group of forearm muscles from the ventral and dorsal groups. A fibrous septum (secondary septum), along which n. medianus runs, oseparates the more superficial and deeper layers of the ventral group of muscles of the forearm.
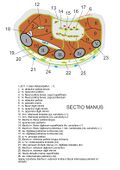
Osteofascial spaces of the hand[edit | edit source]
Spatia intermetacarpalia (spatia interossea) are closed using individual metacarpals, fascia dorasalis manus interossea and fascia palmaris interossea. The space between the fascia palmaris interossea and fascia palmaris superficialis is divided into three by means of the radial (attaches from the radial edge of the palmar aponeurosis to the 3rd metacarpal) and ulnar (attaches from the ulnar edge of the palmar aponeurosis to the 5th metacarpus) osteofascial septum of the palmdivided into three spaces: spatium palmare radiale (at the thumb), spatium palmare ulnare (at the little finger) and spatium palmare medium (middle part of palm). Spatium palmare radiale contains the thenar muscles, ends blindly proximally. Spatium palmare ulnare contains the hypothenar muscles, proximally it also ends blindly. Spatium palmare medium contains two layers of flexor tendons, vessels and nerves, proximally it connects with the canalis carpi.
Gallery[edit | edit source]
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
Resources[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír. Anatomie I. 2. edition. Grada, 2001. 516 pp. ISBN 978-80-7169-970-5.