Melanocytic tumors
From WikiLectures
Melanocytic tumors belong to the neuroectoderm tumors. They arise from melanocytes, which are cells capable of producing melanin. Most non-tumor melanocytes are deposited in the epidermis, dermis and hair follicles. However, these cells can also be found in the mucous membranes, eyeball or meninges. They probably arise from pluripotent cells of the neural crest and migrate through the paraspinal ganglia, peripheral nerves to the epidermis.
Melanocytic tumors include non-cellular nevi and malignant melanomas.
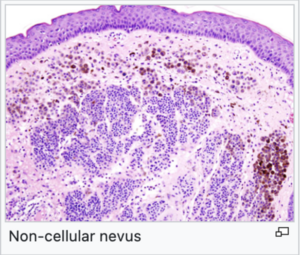
Non-cellular nevi[edit | edit source]
- These are benign tumors occurring mainly in the skin, mucous membranes and eyeball.
- They most often occur in the skin, where we call them a birthmark or melanocytic nevus.
- They may be congenital or acquired, where acquired are more common and are associated with UV radiation and inflammatory cytokines.
- under the microscope, they look like nests of accumulated melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis or in various parts of the dermis.
Malignant melanomas[edit | edit source]
- They are malignant tumors.
- They occur less often than non-cellular cells, but their incidence increases faster than other tumors.
- It is one of the tumors with the worst prognosis.
- They can occur in the skin, eyeballs, and meninges.
- They rarely occur around the prostate or internal genitalia of women, in the mucous membranes of the oral, nasal and distal rectum.
- Tumor cells have an atypical character (prominent nuclei and nucleoli) and increased mitotic activity, including atypical mitoses.
- Tumor cells can grow.
- Superficially spreading melanoma - grows horizontally and does not reach deeper layers.
- Nodular melanoma - spreads vertically and extends into the deeper layers and subcutaneous adipose tissue.
- Lentigo maligna melanoma - spreads radially and later vertically, is typical of the elderly.
- Malignant melanoma looks like a birthmark with irregular edges , irregularly colored. It may itch or hurt , and gradually increases.
- In the advanced stage, melanoma has a dark color.
- Melanocytes are irregularly distributed at different heights of the epidermis.
- Tumor margins are formed by individual melanocytes.