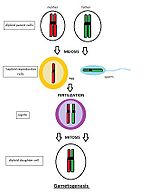
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis is a process of formation of gametes – reproduction cells. The gametes are created in special type of the cell division called meiosis. During meiosis the diploid parent cell divides into haploid daughter cells. Haploid cell has just one set of chromosomes (23 pairs). The fetus is created by fusion of two haploid cells – a womans egg and mans sperm. Each cell of fetus is then diploid – it contains 46 chromosomes.
Variability of Gametogenesis[edit | edit source]
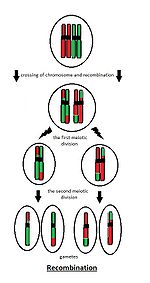
Children have one set of chromosomes from each parent. But information which is transferred is not always the same. That is the reason why siblings don´t look like each other or like their parents. Gametogenesis is extremely variable process. During the meiosis the maternal and the paternal chromosomes are crossing on many places. While they are connected the recombination starts. This process is called crossing over.
Recombination in many parts of 23 chromosomes brings thousand possibilities of gametes. Gametes include a mixture of maternal and paternal genetic information. This fact is very useful for the offspring. Diversity in their genome gives them some advantages or disadvantages. It is the way how to guarantee that at least some of them survive.
During meiosis (reproductive cells division) it is necessary to split the diploid cell into the daughter haploid cells correctly. Sometimes we can find some disproportion which leads to chromosomal abnormalities. Some of the reproductive cells include or miss a chromosome. Most common disorders are monosomies and trisomies, e.g. Down syndrome (trisomy 21).
Processes Leading to Variability[edit | edit source]
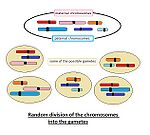
Random distribution of chromosomes[edit | edit source]
- During meiosis the maternal and the paternal chromosome are randomly divided into the gametes.
- Potentially it can be produced 2n gametes.
- In human it means 223, that is 8,4 x 106 gametes.
Recombination[edit | edit source]
- The number of gametes is higher in fact due to recombination.
- Two or more recombinations occur on each chromosome.
- Then one chromosome includes paternal and also maternal parts.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Bibliography[edit | edit source]
- ALBERTS, Bruce. Základy buněčné biologie. 2.vydání edition. 1998. ISBN 80-902906-2-0.