Femoral Artery
 A. femoralis passing in the lacuna vasorum | |
| A12.2.16.010 | |
| a. epigastrica superficialis, a. circumflexa ilium superficialis, aa. pudendae externae, a. profunda femoris, a. descendens genus | |
| a. poplitea |
A. femoralis is a continuing artery a. iliaca externa from lig. inguinale. AND. femoralis passes through the lacuna vasorum, where it is located centrally next to the nervus femoralis, which lies most laterally and runs through the lacuna musculorum. AND. femoralis then runs into the popliteal fossa through the hiatus adductorius. V. femoralis, on the other hand, is located more medially and gradually passes behind the artery until it reaches the outer side.
According to the course, a. femoralis has three sections:
- Part in trigonum femorale and fossa iliopectinea
- Section under m. sartorius
- The last part from the canalis adductorius to the hiatus tendineus
A sensitive branch from the femoral nerve - the saphenous nerve accompanies the artery to the last two sections.
Supply area[edit | edit source]
A. femoralis and its branches supply the skin of the anterior lower abdomen, the anterior region of the scrotum or labia, all structures of the thigh including the knee joint.
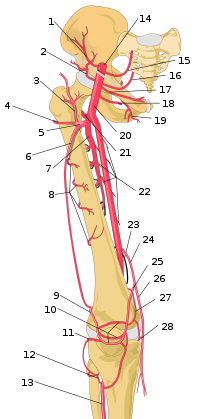
1 – A. circumflexa ilium profunda
2 – A. circumflexa ilium superficialis
3 – R. ascendens, a. circumflexa femoris lateralis
4 – R. transversus, a. circumflexa femoris lateralis
5 – A. circumflexa femoris lateralis
6 – R. descendens, a. circumflexa femoris lateralis
7 – A. profunda femoris
8 – Rr. perforantes
9 – a. superior lateralis genus
10 – patellar anastomoses
11 -a. inferior lateralis genus
12 – R. circumflexus fibulae, a. tibialis anterior
13 – A. tibialis anterior
14 – A. iliac externa
15 – A. epigastrica inferior
16 – A. epigastrica superficialis
17 – A. pudenda externa superficialis
18 – A. pudenda externa profunda 19 – A. obturatoria
20 – A. femoralis
21 – A. circumflexa femoris medialis
22 – Rr. musculares
23 – Hiatus adductor
24 – A. descendens genus
25 – R. articularis, a. descendens genus
26 –R. saphenus, a. genus descendens
27 – A. superior medialis genus
28 – A. inferior medialis genus
Branches[edit | edit source]
Superficial epigastric artery[edit | edit source]
A thin branch that ascends and branches into the hypodermis toward the navel.
Arteria circumflexa ilium superficialis[edit | edit source]
It passes through the subcutaneous tissue of the thigh along the ligaments. inguinale to spina iliaca anterior superior.
Arteriae pudendae externae[edit | edit source]
Two branches, one of which bends into the pubic landscape and the other sends out:
- rr. scrotales/labiales anteriores to the external genitalia.
Arteria profunda femoris[edit | edit source]
A very strong main artery for the muscles of the thigh, which departs laterodorsally about 3–5 cm below the lig. inguinale – but the distance can be quite variable. Broadcasts:
- a. circumflexa femoris medialis' - passes into the fossa iliopectinea, back to the hip joint and for the pelvitrochanteric muscles, posterior thigh muscles and adductors.
- a. circumflexa femoris lateralis' - continues under m. rectus femoris and supplies all components of m. quadriceps femoris
- r. descendens - branch of the artery descending to the knee joint.
- aa. perforantes' - final branches that pass to the dorsal side through the slits between the adductor attachments. They supply the adductors and all the muscles of the dorsal group, at the same time the aa. nutriciae femoris emerge from them.
Arteria genus descendens[edit | edit source]
It departs in the canalis adductorius, then it is joined by the vein and the n. saphenus'' and together breaks through the membrana vastoadductoria. Its supply area is the muscles of the thigh and it is added to the vascular network of the knee joint - rete articulare genus. In addition to the main branches, there are also small branches for the inguinal lymph nodes and muscle branches.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related Articles[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ČIHÁK, Radomír – GRIM, Miloš. Anatomie 3. 2., upr. a dopl edition. Grada, 2004. pp. 673. ISBN 80-247-1132-X.
