Fanconi's syndrome
Fanconi's syndrome is a disease of the kidney tubules. It was named after Guido Fanconi , a Swiss pediatrician.
![]() Not to be confused with Fanconi's anemia , which is another disease.
Not to be confused with Fanconi's anemia , which is another disease.
Characteristics[edit | edit source]
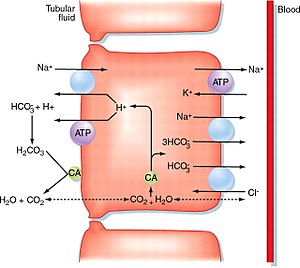
Disease of the proximal tubules of the kidneys, in which the reabsorption of some important substances in the proximal tubule is impaired. Reabsorption disorders are manifested by increased excretion of a number of important substances in the urine of glycosuria, phosphaturia, aminoaciduria , bicarbonaturia. Renal tubular acidosis of the proximal type. Subsequently, disorders of the mineral economy or acid-base balance develop . Clinically, it manifests itself in metabolic disruption, acidosis, dehydration. Phosphate deficiency is manifested mainly by bone diseases, namely osteomalacia, rickets, osteoporosis, growth disorders. Sodium loss leads to orthostatic hypotension, hypokalaemia can lead to muscle weakness.
Symptoms[edit | edit source]
- Polyuria, polydypsy, failure to thrive;
- growth retardation;
- hypokalaemia due to secondary hyperaldosteronism
Therapy[edit | edit source]
Therapy consists of substitution of substances excreted in the urine.
Types[edit | edit source]
- Congenital - cystinosis, galactosemia, Wilson's disease , hereditary fructose intolerance;
- acquired - heavy metal poisoning, myeloma, nephrotic syndrome, drugs (cisplatin, gentamicin, azathioprine).
Links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- TESAŘ, Vladimír – SCHÜCK, Otto. Klinická nefrologie. 1. edition. Grada, 2006. ISBN 80-247-0503-6.
- VOKURKA, Martin – HUGO, Jan. Fanconiho syndrom [online]. Maxdorf, ©2009. [cit. 2011-04-30]. <http://lekarske.slovniky.cz/pojem/fanconiho-syndrom>.
- KLENER, Pavel. Vnitřní lékařství. 4. edition. Galén : Karolinum, 2011. 1174 pp. ISBN 978-80-7262-705-9.