External acoustic meatus and tympanic membrane
The ear is the organ responsible for hearing and balance (equilibrium). It is divided into 3 parts: external ear, middle ear and internal ear.
The external and middle ear are concerned mainly with the transfer of sound into the internal ear, where the organ of hearing is located.
The Auricle (pinna)
Composed of irregularly shaped plate of elastic cartilage with perichondrium, covered by a thin layer of skin. Lobule of the auricle: not cartilaginous - fibrous tissue, fat and blood vessels.
Blood supply of auricle
- Branches from the superficial temporal artery
- Branches from the posterior auricular artery
Innervation
Sensory innervation:
- Great auricular nerve (from cervical plexus)
- Auriculotemporal nerve (from mandibular nerve)
- Vagus nerve
- Facial nerve
- Lesser occipital nerve (from cervical plexus)
External acoustic meatus
A canal (2-3 cm) that leads to the tympanic membrane.
The canal is wave-shaped:
Lateral 1/3: Cartilaginous (elastic), lined with skin that is continuous with the auricle - contains ceruminous glands and sebaceous glands that produce cerumen (ear wax).
Medial 2/3: Bony, lined with skin that is continuous with the tympanic membrane.
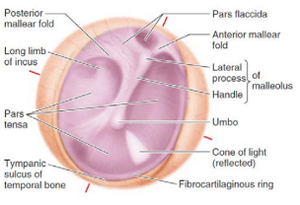
Tympanic membrane
Covered externally by thin skin and internally covered by mucosa of the middle ear.
It is concave in otoscopic view, positioned obliquely inside the meatus.
- The umbo: the peak of a large depression in the center
- Mallear stria: handle of malleolus
- Mallear prominence: lateral process of malleolus
- Anterior and posterior mallear folds: formed by the connection with the malleus
The rest of the membrane is classified as:
- Pars tensa (tensed membrane)
- Pars flaccida (loose membrane): forms the superior recess of the middle ear.
Cone of light: an area light reflects during examination
Paracentesis:
The sampling of fluid using a needle from the middle ear. Usually during infection after unsuccessful treatment with antibiotics.
Myringotomy:
A surgical procedure in which a small incision is made in the tympanic membrane - usually in the posterior-inferior quadrant to avoid damage to the chorda tympani (passing through the middle ear). The procedure is used to drain fluid or pus from the middle ear, and to ventilate it.Very often the procedure is followed by tympanostomy - the insertion of a small tube in the hole made.