Compton scattering of X-rays, apertures
Compton scattering of X-rays[edit | edit source]
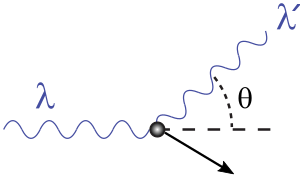
In principle, Compton scattering of X-rays is not significantly different from gamma-ray scattering. In the end, this discovery was first observed in X-rays already in the first half of the 20th century. In general, the principle of Compton scattering is the ejection of an electron by a photon. In order for the reaction to take place, only a certain amount of photon energy is consumed. This is the fundamental difference between Compton scattering and the photoelectric effect, where all the energy of the radiation is used to eject an electron from an atomic shell. The photo effect can therefore only occur once for a given photon, while Compton scattering simply continues until the photon has enough energy to knock out an electron. With each collision, it loses some energy and at the same time is "distracted" - it continues to move along a different path independent of the original path. Therefore, this phenomenon is also referred to as Compton scattering.
X-ray screens[edit | edit source]
Screens are devices for eliminating the ionizing effects of X-ray radiation. It is divided into primary and secondary:
a) Secondary aperture
- It serves to narrow (regulate) the X-ray beam.
- It reduces the dose of ionizing radiation to the patient.
- It is composed of several pairs of lead lamellae and is fixed on the exit window of the X-ray machine .
b) Secondary aperture
- It captures secondary radiation resulting from the interaction of X-ray radiation with tissues in the patient's body (it will only pass if it has the same direction as the primary radiation).
- It is also composed of lead lamellas located closer to the patient.
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
- Compton's phenomenon - what it proves and benefits
- The Compton effect - what does it consist of
- Compton scattering
- Fluoroscopy
- Skiagraphy
Resources[edit | edit source]
- BENEŠ, Jiří – JIRÁK, Daniel – VÍTEK, František. Základy lékařské fyziky. 4. edition. Praha : nakladatelství Karolinum, 2015. ISBN 978-80-246-2645-1.
- NAVRÁTIL, Leoš – ROSINA, Josef. Medicínská biofyzika. 1. edition. Praha : Grada Publishing, 2005. ISBN 80-247-1152-4.