Cardiac markers
From WikiLectures
Diagnosis of MI[edit | edit source]
The most serious type of ischemic injury is acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Transient and fully reversible myocardial ischemia is called angina pectoris . Clinical manifestations:
- Pain in the chest
- Changes on ECG
- Changes in biochemical markers
Classical tests in the diagnosis of MI[edit | edit source]
| Test enzyme | Standard | The beginning of the rise | Maximum | Standardization | Multipler at maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) | < 0,67 μkat/l | 4–8 h | 16–48 h | 3–6 days | Up to 25 |
| Creatine kinase (CK) | men < 3,2 μkat/l | 3–6 h | 16–36 h | 3–5 days | Up to 25 |
| women < 2,4 μkat/l | |||||
| CK-MB isoenzyme | < 0,4 μkat/l, < 6 % of total CK activity | ||||
| Lactate dehydrogenase(LD) | < 8 μkat/l | 6–12 h | 24–60 h | 7–15 days | Up to 8 |
| LD isoenzymes |
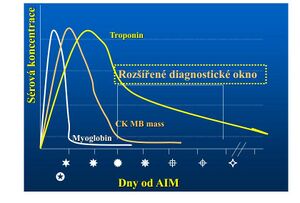
New tests in the diagnosis of MI[edit | edit source]
- cytoplasmic protein, source of O2 in the anaerobic phase of contraction
- in the blood 0.5-2 h after MI (sensitivity 4-5 h)
- small molecule (Mr = 17,100), rapidly lost from the blood through the glomeruli
- standard
- M < 92 µg/l
- F < 76 µg/l
- CK-MB mass isoenzyme (antigen determination)
- concentration is given in mass units (µg/l) !!
- degraded molecules also react to the antigen (higher sensitivity)
- standard: < 5 µg/l
| Test enzyme | The beginning of the rise | Maximum | Standardization | Multiplier at maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Myoglobin | 0,5–2 h | 6–12 h | 0,5–1 d | Up to 20 |
| Troponin T | 3,5–10 h | 12–18 h (3–4 d) | 7–20 d | Up to 300 |
Recommended procedure for biochemical examination in suspected AMI[edit | edit source]
- First recruitment on admission - STATIM
- Basic parameters for broader differential diagnosis: Na, K, Cl, urea, creatinine, Ca, uric acid, cholesterol, TAG, total bilirubin, ALT, AST, ALP, GMT, LD, CRP
- Cardiac markers:
- CK, CK-MB
- Myoglobin – difficulties lasting 2-12 hours, normal renal function
- Troponin T:
- a) within 8 hours to exclude AMI
- b) after 12 hours to diagnose microinfarcts
- Further recruitment
- 2. Recruitment in 6 ± 2 hours (CK, CK-MB, troponin T, Myoglobin)
- 3. Recruitment in 12 ± 2 hours (CK, CK-MB if the diagnosis or extent of involvement is not clear)
- 4. Recruitment in 24 ± 2 hours - exceptionally
Interpretation of results[edit | edit source]
Myoglobin[edit | edit source]
- < 30 µg/l
- normal in healthy, excludes AMI between 6 and 10 hour
- 30–70 µg/l
- if the concentration rises to less than 40 µg/l within 1 h, MI can be ruled out
- > 70 µg/l
- excluding skeletal muscle damage, MI
Troponin T[edit | edit source]
- < 0.05 µg/l - MI can be excluded, repeat in 10-12 h
- 0.05-0.1 µg/l - it is recommended to repeat testing in 1 hour
- 0.1-3 µg/l - myocardial damage
- > 3 µg/l - massive myocardial damage
Troponin I[edit | edit source]
- <0.1 µg/l - MI can be excluded
- 0.6-1.5 µg/l - according to the WHO this is evidence of MI
| Analyze | Myocardial reperfusin | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Successful | Unsuccessful | ||
| C1–C0 (µg/l) | Tmax–T0(h) | Tmax–T0(h) | |
| Myoglobin | > 150 | < 3 | > 12 |
| CK MBmass | > 10 | < 8–12 | > 12 |
| Troponin T | > 0,2 | < 14 | > 14 |
| Troponin I | > 100 | < 14 | > 14 |
Natriuretic peptides[edit | edit source]
- Hormones synthesized in atrial and ventricular cardiomyocytes
- Maintain electrolyte and volume homeostasis
- ANP, BNP - produced by cardiomyocytes
- CNP - produced by vascular endothelial cells and renal epithelium
Links[edit | edit source]
Related articles[edit | edit source]
Resource[edit | edit source]
- MRAZOVA, K. Kardiomarkery [online]. [cit. 2012-03-15]. <https://el.lf1.cuni.cz/p67526721/>.