Blood Pressure
Basic Concepts[edit | edit source]
Blood Pressure – the force exerted by the blood against a unit of area of the vessel wall (in mmHg)
During each heartbeat, the blood pressure changes between two values:
- a maximum – SYSTOLIC PRESSURE – the pressure when the heart releases the blood in the vessels - about 120 mmHg
- a minimum – DIASTOLIC PRESSURE – pressure in the blood vessels between each heartbeat (when the heart is resting) - about 80 mmHg
Pulse Pressure – the difference between systolic and diastolic pressures (40 mmHg)
Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) – the average pressure within an artery over a complete cycle of one heartbeat
MAP = Diastolic Pressure + 1/3 Pulse Pressure
Total Peripheral Resistance - the sum of the resistance of all peripheral vasculature in the systemic circulation.
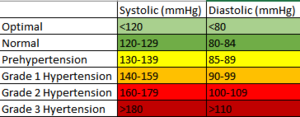
A healthy adult's pressure should not be higher than 140/90 mmHg. High pressure is called hypertension and low pressure is called hypotension.
- Blood pressure in selected parts of the circulation
| Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Aorta | 120 | 80 |
| Left ventricle | 120 | 0 |
| Pulmonary artery | 25 | 8 |
| Right ventricle | 25 | 0 |
Measurement of Blood Pressure[edit | edit source]
Blood pressure can be measured in several ways: directly (invasively), indirectly, and automatically. For automatic measurement, we can use the auscultation method and the oscillometric method.
Regulation of Blood Pressure[edit | edit source]
There are 2 main mechanisms that regulate blood pressure:
- Short/Fast Term Mechanism - Neurally mediated baroreceptor mechanism that regulate blood vessel diameter, heart rate and contractility
- Slower/Long Term Mechanism - Hormonally regulated renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism that regulate blood volume
Fast Term Mechanism[edit | edit source]
- Is a negative feedback system that is responsible for the minute to minute regulation of arterial blood flow
- The sensor for MAP is provided by baroreceptors (stretch receptors) located in the carotid sinus and aortic arch
- Sensitive between 80 – 150 mmHg
Long Term Mechanism[edit | edit source]
- Slow hormonal mechanism by adjustment of blood volume
- Renin – angiotensin – aldosterone System
Summary[edit | edit source]
- BP: FORCE EXERTED BY BLOOD AGAINST ANY UNIT AREA OF THE VESSEL WALL
- BP HAS DIFFERENT VALUE THROUGH THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
- ARTERIAL PRESSURE PULSATION: 120/80 mmHg
- REGULATION VIA AUTONOMIC AND HORMONAL SYSTEM
- BP IS CONTINUALLY CHANGING DEPENDING ON ACTIVITY, TEMPERATURE, DIET, PHYSICAL OR EMOTIONAL STATE, MEDICATION…
References[edit | edit source]
Guyton, Arthur C.; Hall, John E. Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology. 12th ed. USA: Saunders, 2011. GUYTON, Arthur C, et al. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 12th edition. USA : Saunders, 2011. [1] [2]